
[ad_1]
The transient’s key findings are:
- IBM has reopened its outlined profit plan to make use of the plan’s surplus – quite than company money – to fund retirement contributions.
- This shift has been fueled by a extra favorable regulatory atmosphere and the improved funded standing of outlined profit plans.
- Whereas utilizing “trapped surpluses” helps the agency, staff could properly come out behind until the positive factors are shared.
- Apparently, the evaluation finds that solely a handful of different massive firms are possible candidates to observe IBM’s lead.
- Thus, the transfer needs to be seen as a monetary maneuver, not a significant change within the provision of retirement revenue.
Introduction
Enthusiasm appears to be rising to reopen – or a minimum of to cease closing and freezing – outlined profit retirement plans. The impetus comes from a extra benign regulatory atmosphere and the improved funded standing of those plans, even earlier than the current rise in rates of interest. Reopening plans permits employers to make use of surplus belongings, which if reverted to the sponsor can be topic to a 50-percent excise tax along with the employer revenue tax. Probably the most dramatic manifestation of this enthusiasm for reopening plans has been IBM’s announcement to shift its 401(ok) match to an computerized contribution to the money stability element of its beforehand frozen outlined profit plan.
This transient lays out the implications of IBM’s shift for the corporate and its staff, and speculates about which firms would possibly observe IBM’s lead. Particularly, the dialogue proceeds as follows. The primary part describes the altering regulatory atmosphere and monetary standing of single-employer outlined profit plans. The second part supplies the main points of IBM’s startling transfer and its implications for each employers and staff. The third part identifies massive overfunded plans that might observe IBM’s lead.
The ultimate part concludes with two factors. First, plan sponsors clearly acquire by placing the “trapped” surpluses to make use of, however, with out some sharing of the positive factors, staff could properly come out behind. Second, amongst main firms, solely a handful are possible candidates to reopen their outlined profit plans. The nation’s largest banks lead the checklist: Financial institution of America and JPMorgan Chase are significantly properly positioned, however Citigroup can also be a risk. Two non-financial corporations – Honeywell Worldwide and Deere & Co. – are additionally potential candidates.
Regulatory and Monetary Developments
The shift from outlined profit pensions to 401(ok) plans has been underway since 1981, however throughout the Eighties and Nineties this development mirrored a surge in 401(ok)s – not the closing of outlined profit plans. In truth, the Nineties had been a good time to sponsor an outlined profit plan. Rising asset values allowed sponsors to make little or no money contributions to their pension funds. By the flip of the century, pension belongings amounted to 123 % of liabilities (see Determine 1).
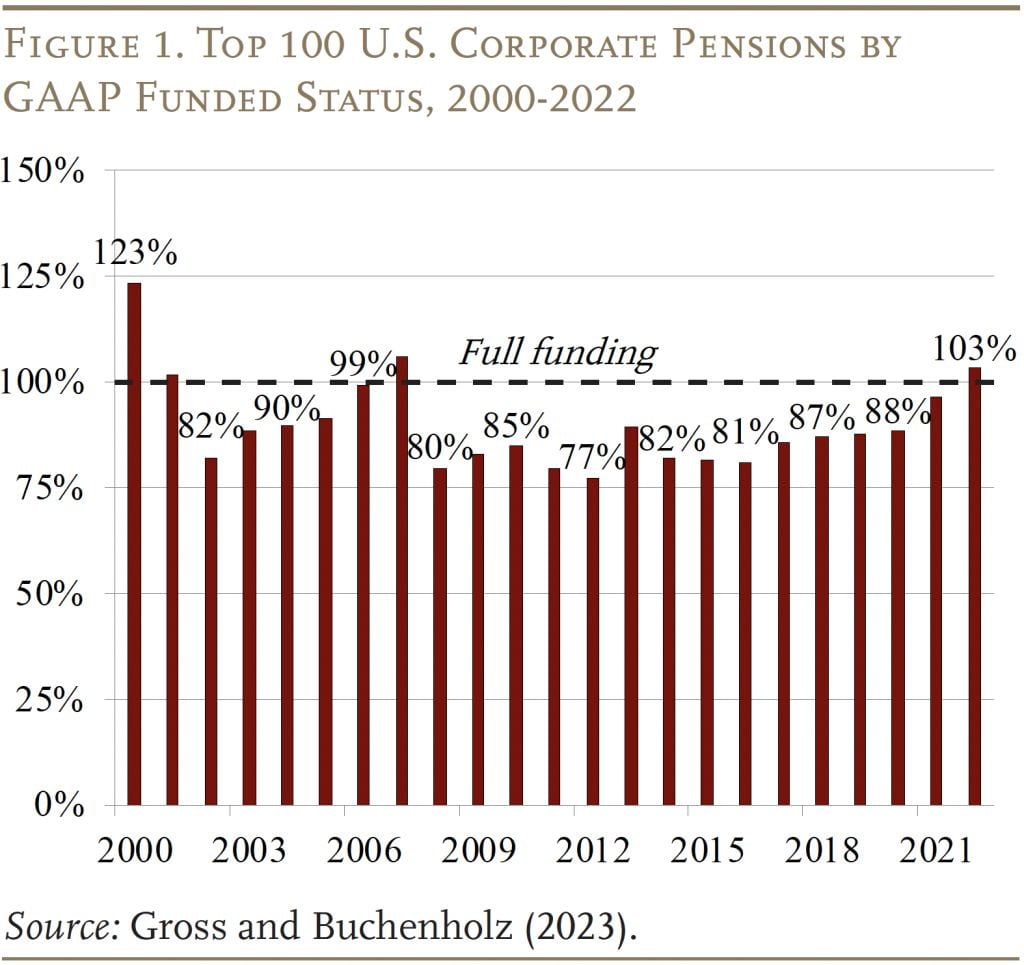
The scene modified dramatically in 2000 when the tech bubble burst and rates of interest tumbled, highlighting the mismatch between belongings and liabilities. In response, Congress tightened funding guidelines within the 2006 Pension Safety Act. For single-employer pension plans, it first set the interval for amortizing all unfunded liabilities at 7 years. Second, it specified three rates of interest for use for discounting promised advantages. The charges, referred to as section charges, rely on when the advantages are anticipated to be paid – in lower than 5 years, 5-20 years, and greater than 20 years. The section charges are company bond yields averaged over the previous 24 months.
On the identical time that Congress tightened funding requirements, the Monetary Accounting Requirements Board modified the reporting necessities, forcing companies to deal with web pension liabilities as debt on their stability sheet.
Shortly after the tightening of funding necessities and the adoption of stricter accounting guidelines, the inventory market and the financial system collapsed within the World Monetary Disaster (2007-2009). With the brand new provisions, the drop in funded standing imposed actual prices on sponsoring companies – their revenue and stability sheets took a success, they usually confronted a pointy enhance in required pension contributions.
In response, company sponsors did two issues. First, they modified their plans’ asset combine, which included shifting away from equities (see Determine 2) and buying bonds that matured as profit liabilities had been projected to fall due (liability-driven funding). On the identical time, they started closing and freezing their outlined profit plans in favor of 401(ok)s. Many outlined profit plan sponsors put themselves on a path to finally get out of the enterprise altogether.
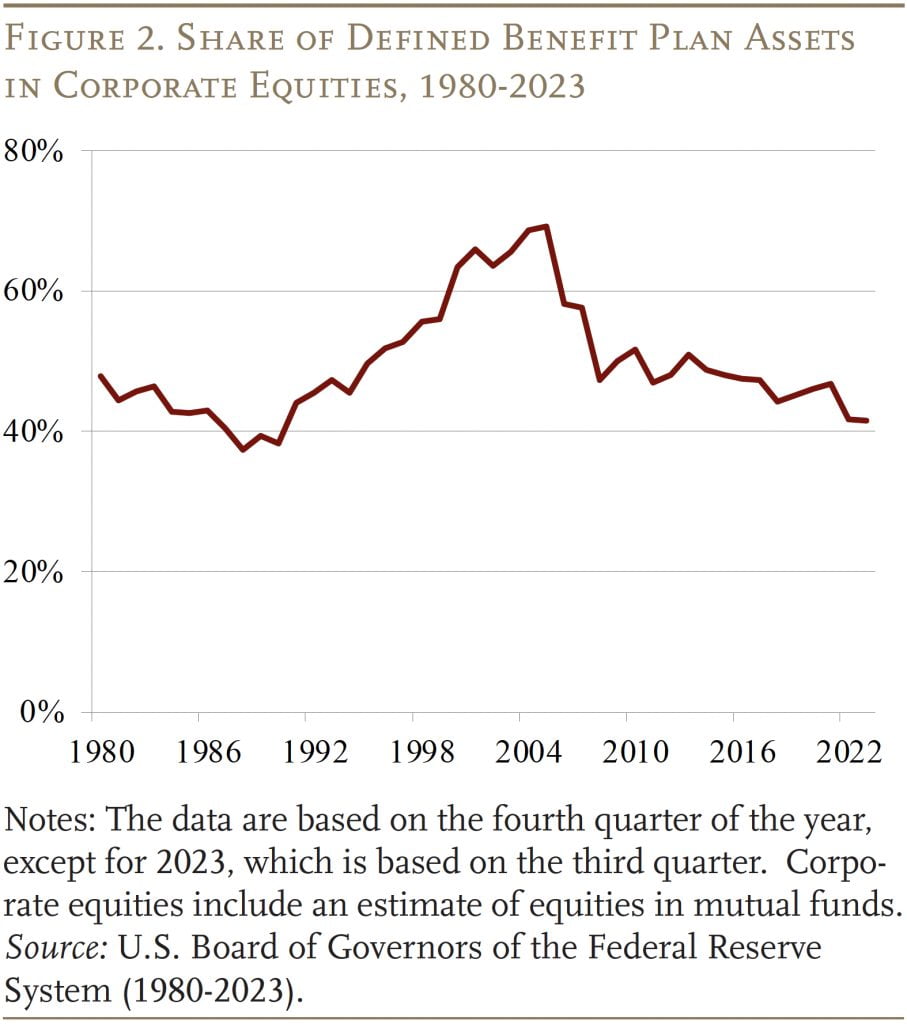
Within the wake of the World Monetary Disaster, two developments made single-employer outlined profit plans extra engaging. First, their funds improved. The change in asset allocation made them a lot much less weak to market swings, and a rising inventory market led to increased asset values. On the identical time, the closing and/or freezing of plans slowed the expansion in liabilities. Because of this, the ratio of belongings to liabilities elevated from a low of 77 % in 2012 to 96 % in 2021. In fact, the spike in rates of interest in 2022 – regardless of poor market returns – boosted funding ranges even additional.
Second, Congress supplied funding aid. The primary essential piece of laws was the 2012 Transferring Forward for Progress within the twenty first Century Act, which permitted the market charge established by the 2006 Pension Safety Act to be averaged over the prior 25 years – a interval when charges had been considerably increased. It additionally established a hall that set the minimal and most charges at 90 % and 110 % of the typical, respectively.
The 2012 laws envisioned the hall widening over time, which – with market charges considerably under the hall – would have decreased the low cost charge and elevated liabilities and minimal required contributions. However further iterations of funding aid prevented this widening from occurring. Because of this, the speed used to calculate liabilities for funding functions has been about 200 foundation factors increased than the “market charge” specified within the Pension Safety Act (see Determine 3).
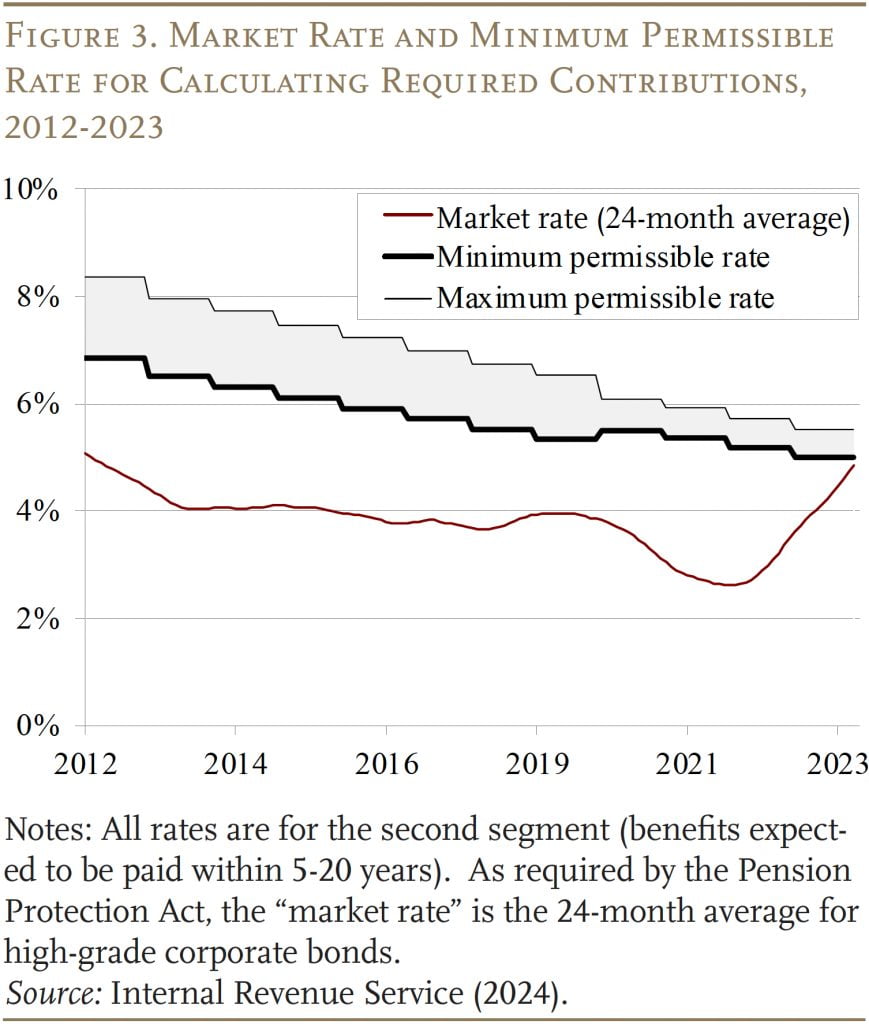
For single-employer outlined profit plans, the second and most dramatic items of funding aid had been included within the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021. First, it set a flooring of 5 % on the 25-year common and narrowed the hall across the common to the vary of 95 % to 105 %. This transformation comes simply because the 25-year common was shifting away from traditionally excessive charges, which might have eradicated the hole between the minimal permissible charge and the “market charge.” The laws additionally completely elevated the amortization interval from 7 years to fifteen years, which will increase the time for underfunded plans to achieve full funding.
A sequence of three influential articles from JPMorgan Asset Administration argue that the improved monetary situation of outlined profit plans – higher funded and fewer dangerous – and the funding aid have “severed the hyperlink” between actions in market rates of interest and required pension contributions. For the reason that concern of enormous required contributions was a significant factor that drove employers away from outlined profit plans, the elimination of contribution threat ought to lead sponsors to rethink potential methods to make use of the “trapped belongings” of their outlined profit plans. It looks as if IBM was listening to this recommendation.
What IBM Did and Why
Beginning in January 2024, IBM ended its 5-percent matching contribution and 1-percent computerized contribution to staff’ 401(ok) accounts in favor of an computerized 5-percent contribution to a “Retirement Profit Account” for every worker. The Retirement Profit Account is the worker’s “notional” account within the money stability element of the corporate’s outlined profit plan. IBM had closed its outlined profit plan to new members in 2005 and “frozen” advantages – that’s, ended new accruals – for current members in 2008.
Money stability plans are outlined profit plans that retain notional particular person accounts till the account is paid out to the person. Like conventional outlined profit plans, the employer makes the contributions and bears the funding threat, whereas the plan fiduciaries handle the investments. As well as, the plan credit the worker’s account with notional earnings, often as curiosity based mostly on the present yield on pre-selected Treasury securities. Workers obtain common statements and sometimes can withdraw the stability as a lump sum once they retire or terminate employment. In contrast to 401(ok) plans, nonetheless, money stability plans are required to supply staff the flexibility to obtain their advantages within the type of an annuity for the worker’s life or for the lifetimes of the worker and the worker’s surviving partner.
Traditionally, IBM had mechanically enrolled new staff in its 401(ok) plan at 5 % of wage after 30 days, until the worker opted out. After one yr, staff then grew to become eligible for IBM’s 5-percent matching contribution and 1-percent computerized employer contribution. Underneath the brand new association, staff obtain a month-to-month credit score of 5 % of pay into their Retirement Profit Account, with the choice to save lots of further quantities via the corporate’s conventional or Roth 401(ok) plans. To compensate for the lack of the corporate’s earlier 1-percent computerized employer contribution, IBM elevated salaries by 1 % efficient January 1, 2024.
The assured charge of notional earnings for IBM’s new Retirement Profit Accounts are as follows:
- first 3 years: 6 % curiosity;
- 2027-2033: yield on 10-year Treasury, with a flooring of three %; and
- 2034 and past: yield on 10-year Treasury.
What Does This Shift Imply for the Firm?
Probably the most important advantage of the shift is that it permits IBM to fund retirement contributions with the excess in its overfunded outlined profit plan quite than with company money contributed to its 401(ok) plan. Based on its annual report, IBM held a surplus of $5 billion in its outlined profit plan, whereas it paid out $530 million yearly in matching and computerized 1-percent contributions to the 401(ok). Confronted with no funding necessities for its over-funded outlined profit plan, IBM can use the $5 billion surplus within the plan to pay for the 5-percent month-to-month credit supplied to staff’ notional particular person accounts for a minimum of the subsequent 10 years – enhancing its money movement assertion by about $500 million annually. Ultimately, IBM must make a contribution to the plan out of firm cash, however good funding efficiency may assist scale back the annual burden.
The drawbacks are modest in comparison with the acquire. First, common actuarial analyses and annual premiums to the Pension Profit Warranty Company make outlined profit plans dearer to function than 401(ok)s. Second, the IBM plan must present the curiosity credit to members’ notional accounts, which, as famous, will quantity to six % within the brief run. These funds are usually not essentially linked to the funding efficiency of the belongings, which would require some hedging effort on the a part of IBM. Third, the discount within the plan’s surplus to fund the month-to-month pay credit will present up as a damaging adjustment within the firm’s monetary statements. Ultimately, IBM must make some funding contributions, however the cost schedule can be way more versatile than the annual contributions to the 401(ok) plan. Alternatively, at that time, the corporate may simply re-freeze the DB plan and revert to the sooner sample of creating money contributions to the 401(ok) plan. In both case, the corporate clearly comes out forward.
What Does This Shift Imply for Workers?
Whereas IBM clearly positive factors from this maneuver, its staff could properly lose. On the constructive facet, staff not collaborating within the present 401(ok) or not maxing out the employer match will certainly acquire, however the positive factors right here can be very small since 97 % of staff at IBM take part within the 401(ok). Equally, the flexibility to obtain lifetime advantages – supplied at very low value – may alleviate among the challenges related to withdrawing 401(ok) balances and buying an annuity. However the positive factors right here rely on what number of members go for the lifetime profit versus the lump sum, and in addition – as within the case of an annuity bought with 401(ok) {dollars} – the worth of lifetime revenue relies upon crucially on what occurs on the inflation entrance. In brief, the potential positive factors for workers are modest.
In distinction, the potential losses for workers are significant. First, if staff don’t modify the asset composition of their 401(ok) contributions, they are going to have an excessive amount of of their belongings in fixed-income investments. After the upper preliminary assure, IBM will present credit equal to the yield on Treasuries. If the corporate’s 5-percent contribution had gone into the 401(ok) as an alternative, it could earn the return on a mixture of shares and bonds – presumably increased. As well as, and not using a match, staff could properly reduce on their 401(ok) saving and find yourself placing much less apart for retirement. On stability, staff are prone to come out behind.
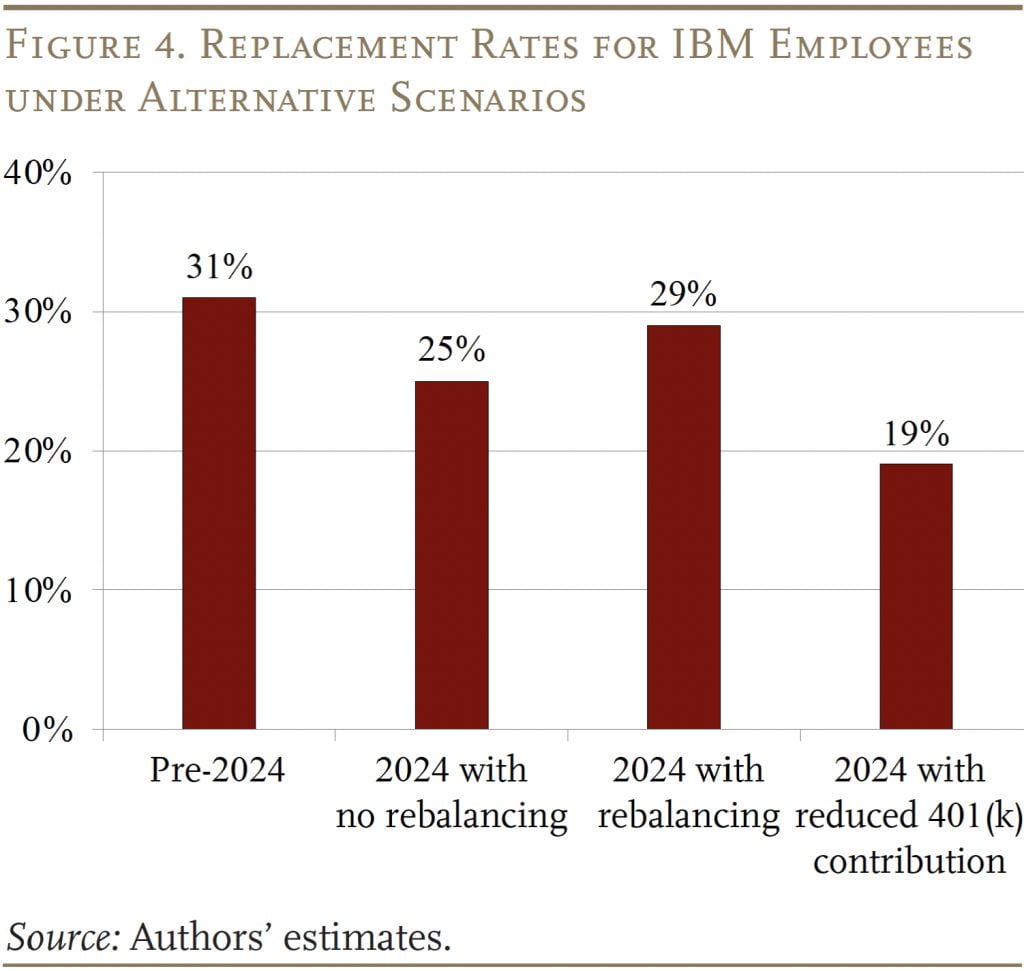
A easy simulation can present some sense of how the worker’s behavioral response can have an effect on the result. The evaluation focuses on a brand new worker who’s age 30 in 2024 and retires at 65. With out IBM’s swap, this worker contributing 5 % to the 401(ok) plan and receiving the 5-percent matching contribution – assuming a portfolio of 60-percent equities and 40-percent bonds – would have a substitute charge of 31 % from the IBM plan at retirement. If the worker now saves 5 % within the 401(ok) invested 60/40 in equities and bonds and 5 % in a money stability plan with IBM’s design (the 10-year Treasury aside from assured returns within the early years), the substitute charge drops to 25 %. If the worker rebalances and places all his 401(ok) belongings in equities, the substitute charge recovers, however not all the best way again as a result of the ratio throughout each plans is 50/50 not 60/40. Lastly, the worker can resolve to save lots of much less within the absence of an employer match. If the worker cuts the 401(ok) contribution to three %, and doesn’t rebalance, the substitute charge drops to 19 %. The vital level is that each one the potential outcomes for the worker are decrease than underneath IBM’s earlier association (see Determine 4).
Will Others Observe?
Will different company sponsors observe swimsuit and reopen their outlined profit plan? As mentioned, IBM’s acquire comes from utilizing the excess in its overfunded outlined profit plan to enhance its money movement by decreasing its ongoing retirement contribution prices. Accordingly, a possible follower ought to have: 1) a big outlined profit surplus that may be put to make use of; and a pair of) massive 401(ok) contributions that, as soon as saved or diminished, can considerably enhance the corporate’s money movement. As well as, an current money stability element within the present closed/frozen plan could make the transition simpler, and a plan that covers non-unionized staff would keep away from the necessity for negotiations.
The evaluation began by wanting on the 45 U.S. firms with outlined profit obligations of greater than $10 billion. Narrowing the main target to closed/frozen plans with a funded ratio over 100% resulted in eight firms. These firms, ordered by their funded ratios, are proven in Desk 1. The desk additionally consists of the excess within the firm’s outlined profit plan, contributions to the corporate’s 401(ok) plan, and two measures which may present an incentive to think about IBM’s strategy – the outlined profit surplus relative to shareholders’ fairness and 401(ok) contributions’ relative to annual money movement. Not surprisingly, IBM ranks excessive on each incentive measures. All firms besides Ford have a significant money stability element of their plans.
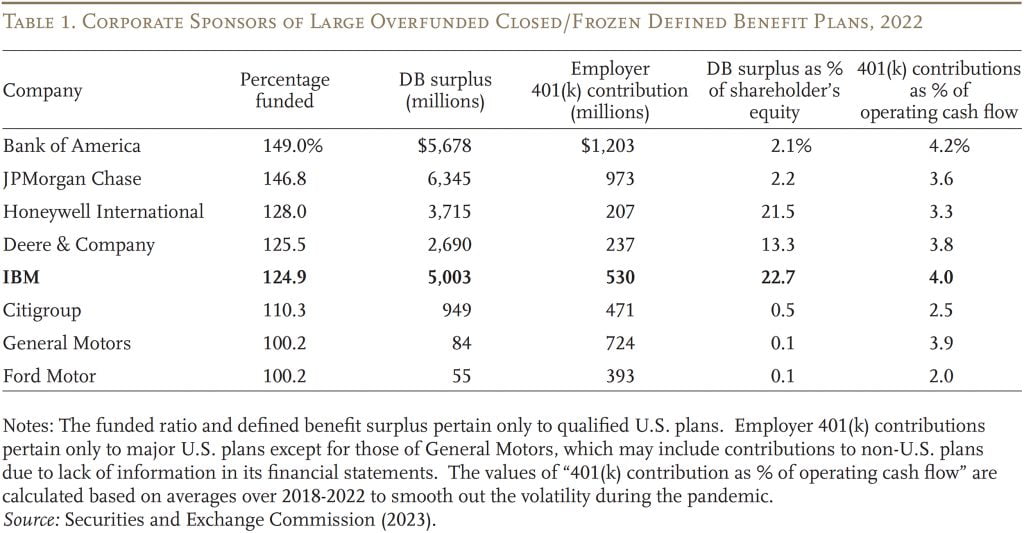
On the highest of the checklist are the nation’s two largest banks – Financial institution of America and JPMorgan Chase. The sheer greenback quantity of their pension surpluses could set off severe consideration of potential various makes use of. Additionally, these firms made massive 401(ok) contributions each in greenback quantity ($1.2 billion and $1 billion, respectively) and as a share of their annual money movement (4.2 % and three.6 %, respectively). These numbers suggest that the potential positive factors from reopening their outlined profit plans may very well be even higher than IBM’s. Citigroup, the fourth largest U.S. financial institution, can also be on the checklist with a funded ratio of 110 %, though its outlined profit surplus and 401(ok) contributions are a lot decrease than the highest two. As few monetary sector staff are unionized, these banks would have nice discretion in setting plan provisions in the event that they determined to reopen the money stability element of their outlined profit plans.
Honeywell Worldwide and Deere & Co., that are third and fourth on the checklist, face a state of affairs just like IBM’s when it comes to the relative sizes of their surpluses and 401(ok) prices. Deere & Co. could not take additional actions anytime quickly because it simply closed its outlined profit plan for salaried staff to new hires in January 2023 and vastly enhanced its 401(ok) matching charge. Nonetheless, down the highway, a speedy enhance in 401(ok) prices may set off a reconsideration of the outlined profit choice.
Common Motors and Ford appear unlikely to observe IBM in reopening their barely absolutely funded outlined profit plans. Restoring their outlined profit plans was really on the checklist of calls for of the United Auto Employees throughout the strike in 2023, and the automakers rejected it. As an alternative, the auto firms agreed to extend their 401(ok) contributions from 6.4 % to 10 % of pay with no required worker contributions. Though Common Motors and Ford are prone to see elevated 401(ok) contributions in coming years, they only do not need the outlined profit surplus wanted to undertake IBM’s strategy.
Total, the large banks – Financial institution of America, JPMorgan Chase, and perhaps Citigroup – and two nonfinancial firms – Honeywell Worldwide and Deere & Co – are the most definitely candidates to reopen their outlined profit plans.
Conclusion
IBM’s shift to reopen its outlined profit plan for retirement advantages is a big growth on the earth of pensions. It’s a monetary maneuver, nonetheless, that enables IBM to fund retirement contributions with the excess in its overfunded outlined profit plan quite than company money; it isn’t a significant change in how the non-public sector supplies retirement revenue. The transfer has been fueled by a extra favorable regulatory atmosphere and the improved funded standing of those plans. Whereas tapping “trapped “surpluses” advantages the corporate, staff face much less flexibility of their funding choices and sure decrease substitute charges. Solely a handful of different massive firms are positioned to observe IBM’s lead. The nation’s largest banks head the checklist: Financial institution of America and JPMorgan Chase are significantly properly positioned, however Citigroup can also be a risk. Two non-financial corporations – Honeywell Worldwide and Deere & Co. – are additionally potential candidates.
References
Congressional Funds Workplace. 2023. The 2023 Lengthy-Time period Funds Outlook. Washington, DC.
Gross, Jared and Mike Buchenholz. 2023. “Pension Defrost: Is It Time to Reopen DB Pension Plans—or at Least Cease Closing and Freezing Them?” Report. New York, NY: JPMorgan Asset Administration.
Gross, Jared and Michael Buchenholz. 2022. “The Roadmap to Pension Stability.” Report. New York, NY: JPMorgan Asset Administration.
Gross, Jared and Michael Buchenholz. 2021. “Rethinking the Pension Plan Endgame: Hibernation, Termination or Stabilization?” Report. New York, NY: JPMorgan Asset Administration.
IBM. 2023. “IBM Advantages 2024 IBM U.S. Advantages Information.” Armonk, NY.
Inside Income Service. 2024. “Pension Plan Funding Segments.” Washington, DC.
JPMorgan Asset Administration. 2024. “2024 Lengthy-Time period Capital Market Assumptions.” twenty eighth Annual Version. New York, NY.
Munnell, Alicia H., Mauricio Soto, J.P. Aubry and Christopher J. Baum. 2007. “Why Are Corporations Freezing Their Pensions?” Working Paper 2007-22. Chestnut Hill, MA: Middle for Retirement Analysis at Boston School.
Securities and Trade Fee. 2023. Monetary Statements filed by varied firms. Washington, DC.
U.S. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. Monetary Accounts of the US, 1980-2023. Washington, DC.
[ad_2]