
[ad_1]
Do you ever drive to a special a part of city and say to your self, “Wow, fuel is a lot costlier right here”?
Or possibly you’ve considered ready to purchase tickets to a sporting occasion in hopes that they’ll drop in value.
Each of those are widespread examples of value discrimination and occur extra usually than you assume. The truth is, a number of companies immediately use retail pricing software program to handle and analyze their pricing methods.
What’s value discrimination?
Worth discrimination is a pricing technique that prices clients various costs for items or companies primarily based on sure standards or what the vendor believes the client will conform to pay.
Sellers interact in value discrimination after they assume that some teams of consumers could be charged completely different costs relying on their traits or the perceived worth of a specific good or service. For instance, the services or products could also be a special value for adults versus senior residents or home consumers versus worldwide consumers.
Journey, healthcare, leisure, and telecommunications are among the sectors that often use value discrimination.
Why is value discrimination essential?
Corporations profit from value discrimination as a result of it encourages clients to purchase extra merchandise whereas additionally luring in different clients who wouldn’t have been earlier than.
The purpose of doing so is {that a} vendor can seize the client surplus. The purpose of value discrimination is to generate probably the most income potential for the services or products they’re providing.
When sellers go about value discrimination, they have a look at the kind of market their services or products is in – that’s, whether or not it’s an elastic or an inelastic market. In an elastic market, the value can change the demand for the product. However, in an inelastic market, the demand will not change when the value adjustments.
When the elasticity of demand is completely different in a single market than in one other, value discrimination turns into worthwhile. This is the reason some companies make the most of demand planning to organize forward of time.
For many who are visible learners, let’s break it down.
If the marginal value (MC) of a services or products is constant throughout all markets, whether or not or not it is divided, it’ll equal the common whole value (ATC). Most revenue happens on the value and output, the place MC equals marginal income (MR).
Nevertheless, if the market is separated, then the value and output of a product in an inelastic market can be P and Q, whereas P1 and Q1 in an elastic sub-market.
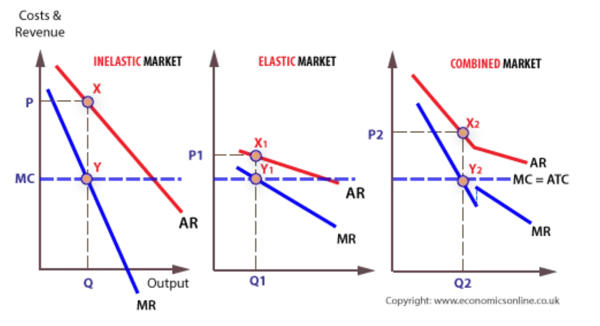
Picture supply: Economics On-line
Kinds of value discrimination
There are three forms of value discrimination which you can encounter: first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree. These levels of value discrimination generally go by different names: customized pricing, product versioning or menu pricing, and group pricing, respectively.
1. First-degree value discrimination
First-degree value discrimination, or good value discrimination, occurs when a enterprise prices the utmost potential value for every unit.
Since costs differ for every unit, the corporate promoting will gather all client surplus, or financial surplus, for itself. In lots of industries, an organization will commit first-degree value discrimination by figuring out the quantity every buyer is keen to pay for a particular product and promoting that product for that precise value. This may be executed utilizing market analysis methods along with utilizing budgeting and forecasting software program.
2. Second-degree value discrimination
Second-degree value discrimination, in any other case generally known as product versioning or menu pricing, occurs when an organization prices a special value for various portions consumed, akin to providing a reduction on merchandise bought in bulk. Merely put, companies value their merchandise consistent with how a lot they will promote.
It does not take a lot work to attract in clients and divide them up into area of interest markets, making this second-degree value discrimination extremely easy to implement. This tactic is utilized by warehouse shops or by telephone corporations that cost further for utilization above a sure month-to-month cap.
3. Third-degree value discrimination
Third-degree value discrimination, or group pricing, is when an organization prices a special value to particular buyer segments akin to college students, navy personnel, or older adults. That is the commonest sort of value discrimination.
Third-degree value discrimination helps corporations decrease extra income by adjusting costs primarily based on particular person clients’ willingness to pay. Final-minute vacationers usually encounter third-degree value discrimination within the tourism and journey trade.
EXAMPLE: Airways usually provide a sure capability for various reserving lessons. Reserving early with low-cost airways usually saves cash. Most airways elevate costs as journey approaches as a result of client demand turns into inelastic. Late bookers often see journey as vital and are keen to pay extra.
Standards for value discrimination
Worth discrimination is just potential below particular market situations.
Imperfect competitors
The corporate should function in a market with imperfect competitors. There must be a sure diploma of monopoly for profitable value discrimination. In a market with good competitors, there can be inadequate energy to have an effect on costs.
Stopping Resale
The corporate should have the ability to stop resale. In different phrases, clients who’ve beforehand bought an merchandise at a reduction can’t resell it to clients who’re more likely to have paid full value for a similar product.
Elasticity of demand
Demand elasticities should differ amongst client teams (i.e., low-income people leaning towards cheap tickets in comparison with enterprise vacationers).
Market segmentation
Market segmentation (age, gender, pursuits, geography, product, time of 12 months) have to be ensured no two markets get intertwined.
Worth discrimination examples
Coupons, age reductions, occupational reductions, retail incentives, and gender-based pricing are a couple of generally seen value discrimination examples for enterprise operations.
- Coupons: Retails assume that clients who gather coupons are extra delicate to the next value than those that do not. By providing coupons, a vendor can cost the next value to clients who do not use coupons whereas additionally offering a reduction to those that do.
- Occupational reductions: Many companies provide decreased costs to those that are presently serving within the navy. The identical could be mentioned throughout a promotion akin to “Nurses Appreciation Week” to those that work within the nursing discipline.
- Age reductions: Most often, reductions are supplied to sure age teams, akin to youngsters, college students, adults, and seniors. A number of institutions don’t cost an age payment for kids below a specified age. Eating places, film theatres, and different forms of leisure are only a few examples of companies that commonly present reductions to clients primarily based on their age.
- Premium pricing: A product that has premium pricing is being bought far past its marginal worth. As an illustration, you might even see a “premium cup of espresso” at your native espresso store that’s priced at $3.50, whereas a daily cup is just $2.
- Retail incentives: These embody rebates, shopping for in bulk, and seasonal reductions. They’re used to extend market share or income on particular merchandise.
- Monetary support: When faculty college students apply for monetary support, the quantity they’re supplied is predicated on their dad and mom’ financial and monetary state of affairs.
- Gender pricing: Sure marketplaces differentiate between genders and set costs accordingly. One instance of this sort of pricing discrimination is the apply of internet hosting a “women’ evening” at a bar or membership.
Advantages of value discrimination
In case you’re a enterprise trying to make the most of value discrimination, some benefits of value discrimination embody:
- Maximizing a revenue: When a value is matched to a particular character inside the market, the revenue is maximized. The enterprise can make the most of the patron surplus inside the market to its benefit.
- Economies of scale: Charging various costs of a product can improve gross sales, because of new shoppers getting into the market.
- Environment friendly use of area: When used appropriately, value discrimination can clear present shares of merchandise sooner, creating a greater use of the shop, store, or manufacturing facility area.
- Understanding the move of consumers: When a enterprise makes probably the most of “completely happy hours” or “early fowl specials”, it encourages clients to regulate their procuring instances in order that they don’t seem to be ready in lengthy traces or procuring throughout busy hours.
Challenges of value discrimination
Alternatively, value discrimination can lead to some disadvantages, too, particularly for the patron. They embody:
- Making the most of particular markets: If a client lives in an inelastic market, it is rather straightforward for them to be exploited and overcharged. An instance can be a client paying a excessive value for a airplane ticket throughout the vacation season.
- Limitations: For shoppers, there are all the time limitations that go hand-in-hand with value discrimination, which may negatively affect the client expertise. For instance, there could be limits to which completely different costs could be utilized, what number of coupons a client can use in the event that they fall into a number of groupings being discriminated in opposition to, and others.
You get what you pay for
Most frequently, all that clients need is to be handled pretty. Clients do have each proper to be outraged in the event that they uncover they’re being charged greater than their next-door neighbor whereas procuring. Nevertheless, it’s protected to say that discriminating in pricing shouldn’t be solely authorized but additionally good enterprise apply.
Normally, clients are misled into considering they’re getting higher offers than they really are. So, generally the value you pay is greater than what another person would pay. It’s extra widespread than you assume and shifting ahead, you’ll hopefully have the ability to spot value discrimination in motion.
Marvel what goes inside a client’s thoughts? Get a greater understanding of how client conduct works!
This text was initially revealed in 2019. The content material has been up to date with new data.
[ad_2]