
[ad_1]
Relational database administration programs (RDBMS) like PostgreSQL and MySQL are vital for storing, organizing, and accessing knowledge for functions and analytics. PostgreSQL and MySQL are fashionable open-source databases with lengthy histories and wealthy characteristic units.
Database
A database is a set of knowledge accessible to computer systems. Databases are used to retailer info equivalent to buyer information, product catalogs, and monetary transactions.
Nonetheless, PostgreSQL and MySQL differ of their technical architectures and design philosophy. Should you’re caught between choosing one database in your software, this information is for you.
We dig into the technical, sensible, and strategic variations between PostgreSQL and MySQL. Let’s get began.
A Temporary Background On PostgreSQL And MySQL
Earlier than diving into the comparisons, let’s briefly introduce PostgreSQL and MySQL.
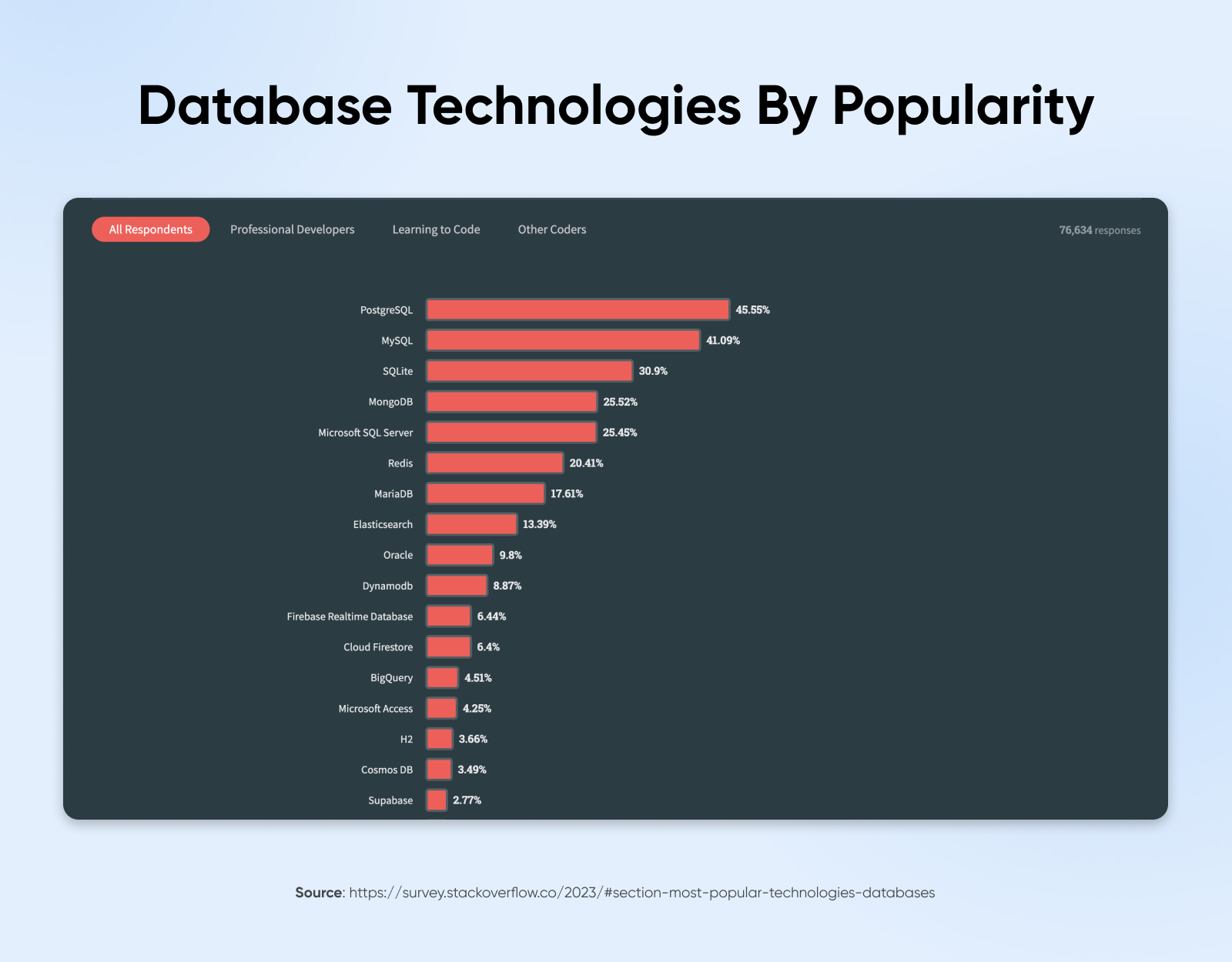
PostgreSQL is an enterprise-level open-source relational database. Utilized by over 45% of the 76,000 respondents within the current StackOverflow developer survey, PostgreSQL overtook MySQL to turn out to be the most well-liked database in 2024.
PostgreSQL emphasizes requirements compliance, extensibility, and confirmed architectures. The PostgreSQL undertaking started in 1986 on the College of California, Berkeley, and has developed options centered on reliability, robustness, knowledge integrity, and correctness.
Postgres employs a five-level system:
- Occasion (additionally referred to as cluster)
- Database
- Schema
- Desk
- Column
Right here is an instance of making a easy customers desk in PostgreSQL and inserting some rows:
CREATE TABLE customers (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(50),
e mail VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO customers (title, e mail) VALUES
('John Doe', 'john@e mail.com'),
('Jane Smith', 'jane@e mail.com');
MySQL is an open-source RDBMS began by the Swedish firm MySQL AB in 1995, which Oracle later acquired. It has historically prioritized velocity, simplicity, and ease of use for creating internet and embedded functions. MySQL’s design emphasizes fast learn and write efficiency.
MySQL employs a four-level system:
- Occasion
- Database
- Desk
- Column
Right here is how one can create the consumer’s desk in MySQL:
CREATE TABLE customers (
user_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(50),
e mail VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO customers (title, e mail) VALUES
('John Doe', 'john@e mail.com'),
('Jane Smith', 'jane@e mail.com');
As you could discover, each queries are related aside from the INT AUTO_INCREMENT altering to SERIAL.
Enjoyable reality: PostgreSQL helps NASA’s “allballs” key phrase (which means “all zeros”) as one other solution to categorical the time at midnight (native and UTC):
postgres=# SELECT 'allballs'::TIME;
time
----------
00:00:00
(1 row)
So, how do these two open-source database titans stack up? Let’s discover additional.
PostgreSQL Vs. MySQL: Efficiency Comparability
Each PostgreSQL and MySQL are able to glorious efficiency, however there isn’t a transparent winner between them.
Should you check learn/write velocity, you’ll discover no consistency in how PostgreSQL and MySQL carry out. It is because database efficiency relies upon closely in your particular workload kind, {hardware} configuration, database schema and indexes, and particularly database configuration tuning. Primarily, the efficiency relies upon drastically in your software’s workload and configurations.
There are 5 common classes of workloads:
- CRUD: Easy READ, WRITE, UPDATE, and DELETE operations.
- OLTP: Transactional, advanced operations of information processing.
- OLAP: Analytical batch processes.
- HTAP: Hybrid transactional and analytics processing.
- Time-Sequence: Time-series knowledge with quite simple, however high-frequency entry patterns.
When working with both of those workflows, you’ll observe that:
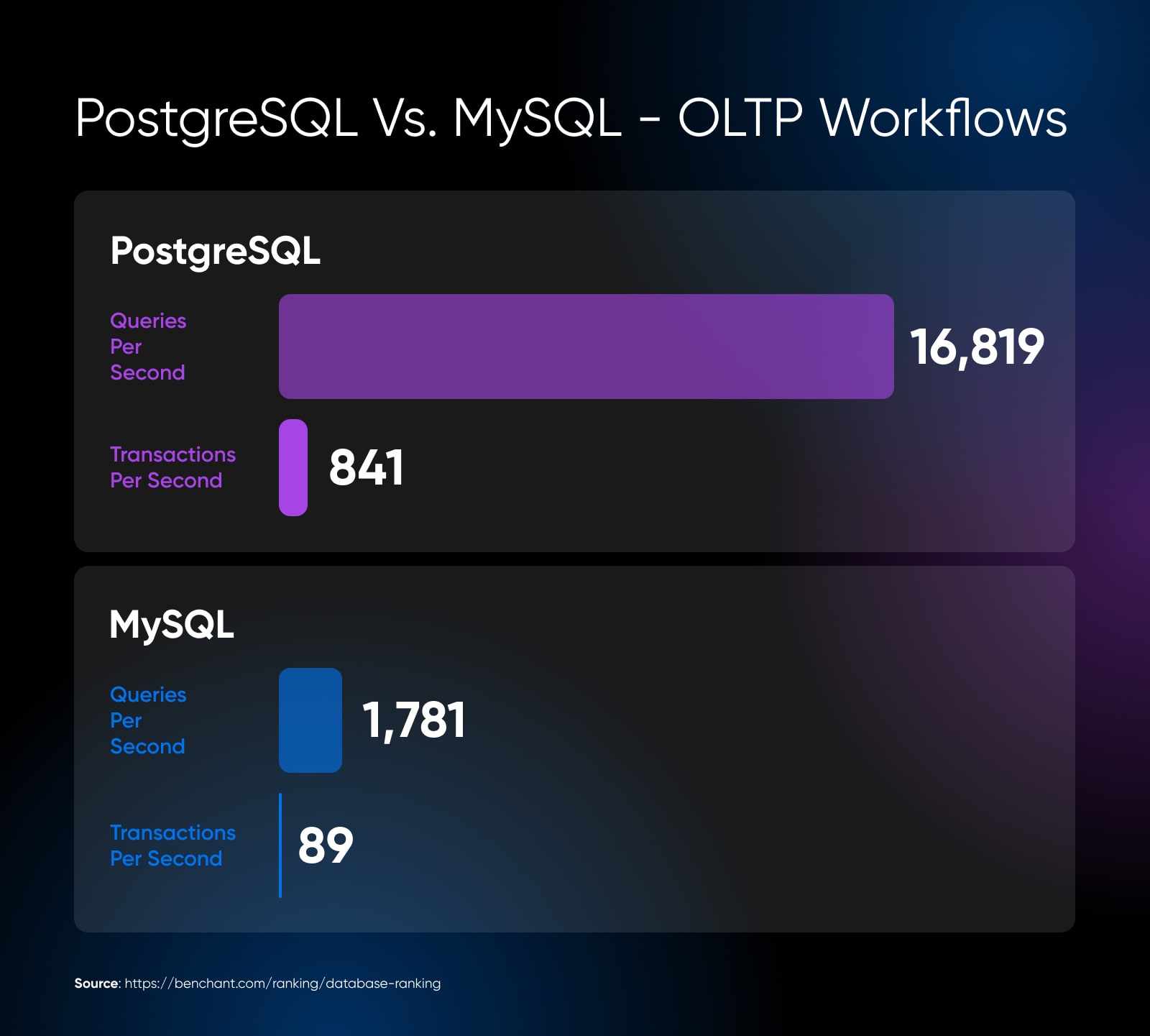
PostgreSQL is thought to deal with heavy OLAP and OLTP workloads fairly effectively. These workloads contain extraordinarily advanced, long-running queries that analyze large knowledge units—for example, enterprise intelligence queries or geospatial evaluation.
“Postgres lets me view a “earlier than the question is executed” plan estimate, in addition to an “after execution” plan. The latter provides me detailed information of how the question truly ran, how lengthy every particular step within the question took, indexes used, and the way a lot reminiscence every step consumed.”
MySQL is mostly good for less complicated CRUD and OLTP workloads involving sooner reads and writes, like internet or cell functions.
Each databases can shine relying on server configuration and your schema for hybrid workloads with a mixture of OLTP and OLAP querying wants.
Question
In databases, queries are requests for particular units of knowledge. Queries can be open-ended questions for knowledge that matches your set parameters.
On the subject of uncooked energy on optimized {hardware}, PostgreSQL typically scales higher to make use of the excessive reminiscence, sooner processors, and extra cores obtainable on the {hardware}.
Learn Efficiency
MySQL typically has sooner learn instances for functions than write operations. Nonetheless, after the current updates to PostgreSQL, it has caught as much as the learn velocity variations.
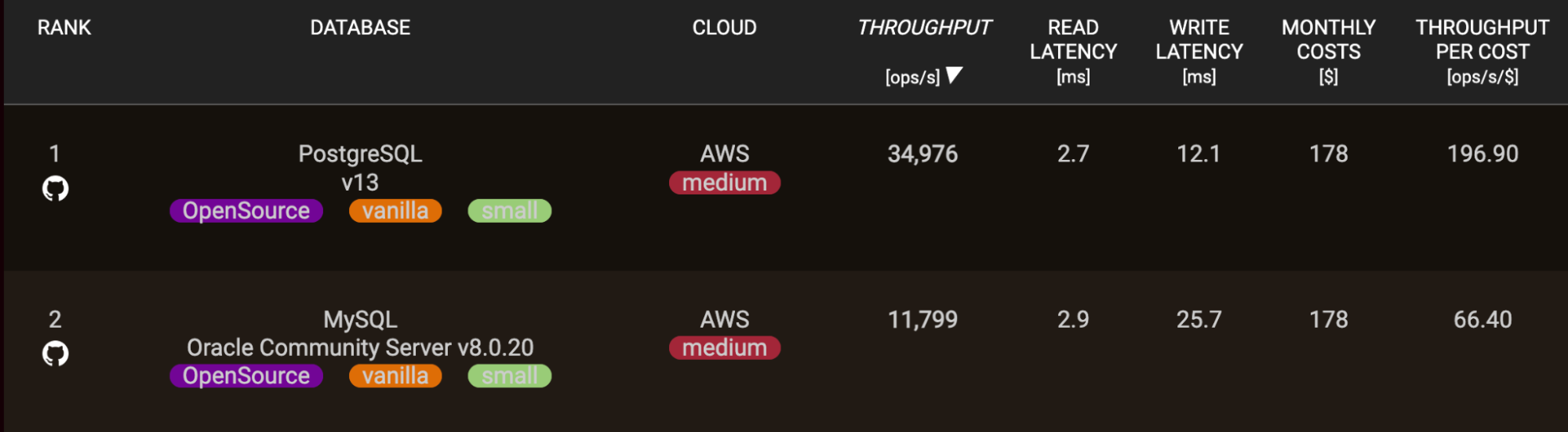
This learn efficiency benefit stems from variations in how the 2 programs are architected — MySQL’s storage engines are extremely optimized for quick single-threaded sequential entry.
After all, with personalized tuning and schemas, PostgreSQL may also ship glorious learn efficiency for a lot of functions. However out of the field, MySQL typically has an edge.
Write Efficiency
On the subject of writing efficiency, together with bulk masses and sophisticated queries that modify knowledge, the overall consensus is that PostgreSQL works higher.
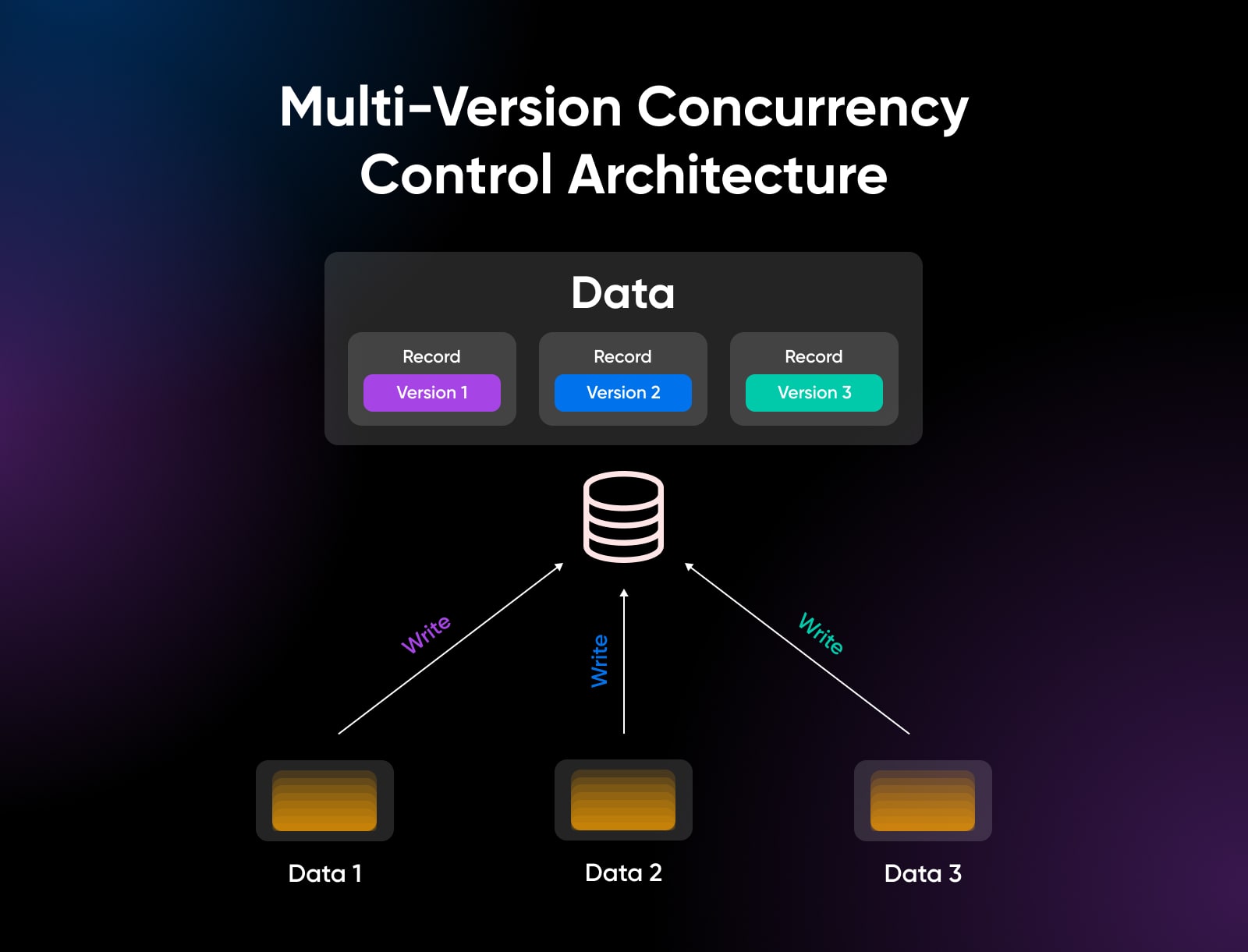
Its multi-version concurrency management (MVCC) structure provides PostgreSQL a serious benefit in permitting a number of periods to replace knowledge with minimal locking concurrently.
In case your software must help many concurrent customers modifying knowledge, PostgreSQL’s write throughput can surpass what MySQL can obtain.
Get Content material Delivered Straight to Your Inbox
Subscribe to our weblog and obtain nice content material identical to this delivered straight to your inbox.
Advanced Question Efficiency
For superior analytical queries that carry out massive desk scans, types, or analytics capabilities, PostgreSQL additionally outshines MySQL in lots of circumstances — and it does so with a big margin.
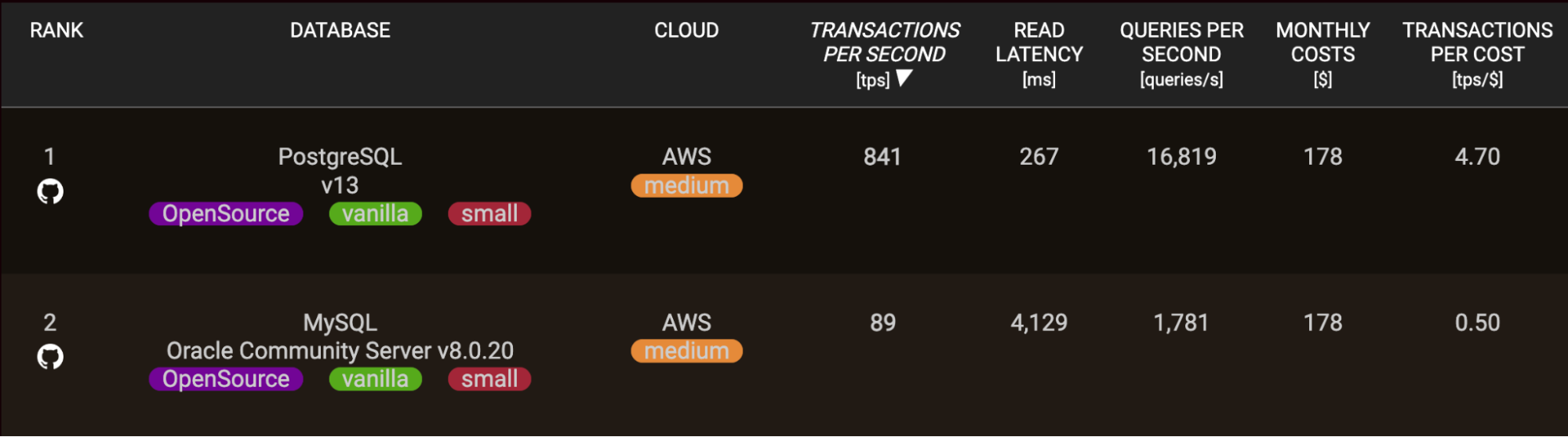
PostgreSQL’s mature SQL question optimizer and help for superior SQL syntax give it a bonus in shortly executing intricate analytic queries. MySQL has considerably improved lately however depends extra on handbook question tuning.
So, for enterprise intelligence or knowledge warehousing wants the place advanced multi-table SQL efficiency issues, PostgreSQL typically excels.
Configuration Impacts Efficiency
After all, databases may be configured and optimized to go well with totally different workloads. So, for any use case, the “finest” system nonetheless relies upon considerably on the underlying server {hardware}, working system, storage subsystem, database configuration, and schema design.
BenchANT does an amazing job of exhibiting how totally different servers can affect a database’s efficiency.
Together with that, the {hardware} configuration additionally makes a big affect in your database efficiency. For instance, for those who use a VPS with NVMe storage, the underlying storage is way sooner than a daily exhausting drive, so your database operations will likely be extraordinarily quick.
Nonetheless, there isn’t a universally quickest system – your mileage will fluctuate based mostly in your atmosphere and tuning.
“Connection administration is the very best argument for MySQL. Nonetheless, there may be truly no actual motive to not use PostgreSQL in any relational use case. That is very true for those who contemplate the developments within the final 3 years. Postgresql is years forward of any competitor in the case of relational databases and even past that. The striving group, amazingly organized supply code, and nearly godlike documentation are solely three of the successful arguments.”
— Reddit consumer, themusician985
When To Contemplate MySQL
MySQL typically outperforms PostgreSQL, utilizing fewer system sources for easy schemas and functions dominated by quick key-value learn entry. Internet and cell functions with extra important wants for scalability, availability, and distributed reads can profit from MySQL’s strengths.
When To Contemplate PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL’s architectural benefits make it price contemplating for workloads requiring advanced write-access patterns, enterprise analytics querying, or flexibility in knowledge sorts. When you’ve got database directors obtainable for configuration and question optimization, PostgreSQL gives a reliable basis.
PostgreSQL Vs. MySQL: Characteristic Comparability
Each databases are full-featured however present appreciable variations in supported knowledge sorts, capabilities, and total characteristic units.
Knowledge Kind Assist
| Characteristic | PostgreSQL | MySQL |
| Knowledge Varieties | Sturdy built-in help for JSON, XML, arrays, geospatial, community, and so forth | It depends extra on JSON extensions |
| Practical Languages | SQL, C, Python, JavaScript | Primarily SQL |
| GIS Assist | Glorious by way of PostGIS spatial extension | Restricted, typically requires add-ons |
PostgreSQL helps a broader set of native knowledge sorts, enabling extra flexibility in your database schemas:
- Geometric sorts for GIS programs
- Community tackle sorts like IPV4/IPV6
- Native JSON and JSONB – optimized binary JSON
- XML paperwork
- Array sorts
- Multi-data-type columns
“Postgres has good array dealing with. So you may retailer array sorts equivalent to an array of ints or an array of varchars in your desk. There are additionally numerous array capabilities and operators to learn the arrays, manipulate them, and so forth.”
— Reddit consumer, mwdb
MySQL has extra fundamental knowledge typing – largely numeric, date/time, and string fields, however can obtain related flexibility by way of JSON columns or spatial extensions.
Practical Languages
PostgreSQL permits capabilities and saved procedures to be written in numerous languages — SQL, C, Python, JavaScript, and extra — for better flexibility.
In distinction, MySQL saved routines have to be coded in SQL, when you can nonetheless write the applying logic in numerous general-purpose languages.
So, if it’s essential embed software logic or advanced calculations immediately into database procedures, PostgreSQL gives way more flexibility.
GIS Assist
For spatial datasets utilized in mapping/geographic functions, PostgreSQL presents glorious built-in performance by way of its PostGIS extension. Location queries, points-within-polygons, and proximity calculations all work out of the field.
MySQL’s spatial help is extra restricted until you undertake a third-party spatial engine like MySQL Spatial or Integration MySOL. For GIS programs, PostgreSQL with PostGIS is mostly a extra easy, extra succesful answer.
Replication
Each databases provide replication, permitting database adjustments to be synchronized throughout occasion. Out of the field, PostgreSQL replication relies on WAL (Write Forward Log) information, which permits web sites to be scaled out to include as many database servers as your coronary heart needs.
So, PostgreSQL makes it simpler to scale out learn replicas finely synchronized with particular knowledge parts that change. For MySQL, third-party instruments could also be wanted.
Structure And Scalability
PostgreSQL and MySQL differ considerably of their total architectures, which impacts their scalability and efficiency profiles.
PostgreSQL’s Object-Relational Mannequin
A key PostgreSQL architectural trait is its adherence to the object-relational mannequin, which implies knowledge can tackle traits much like objects in object-oriented programming. For instance:
- Tables can inherit properties from different tables.
- Knowledge sorts can have specialised behaviors.
- Capabilities are options of information sorts.
This Object-Relational construction permits modeling advanced real-world knowledge nearer to software objects and entities. Nonetheless, it comes at a price — Extra elaborate inside programs are wanted to trace richer knowledge relationships.
The article-relational extensions thus give glorious flexibility, leading to efficiency overhead relative to a strictly relational system.
MySQL’s Pure Relational Mannequin
In distinction, MySQL follows a purely relational mannequin centered round easy knowledge desk schema and relations by way of international keys. This less complicated mannequin interprets to good efficiency for website-driven transactional workloads.
Superior MySQL utilization with intensive JOIN operations or localized enterprise logic is dealt with higher by way of software code reasonably than database customizations. MySQL opts for simplicity over flexibility in its core structure.
In contrast to PostgreSQL, MySQL is a purely relational database with out object-oriented options. Every database consists of particular person tables with no inheritance or customized sorts. JSON has lately offered some doc database flexibility.
Nonetheless, by avoiding object options, MySQL achieves greater out-of-the-box efficiency in lots of workloads, nevertheless it lacks PostgreSQL’s deeper modeling capabilities.
So, MySQL is quicker for easy knowledge, whereas PostgreSQL adapts higher to complexity. Select based mostly in your knowledge entry and scaling wants.
Write Scaling With Multiversion Concurrency Management (MVCC)
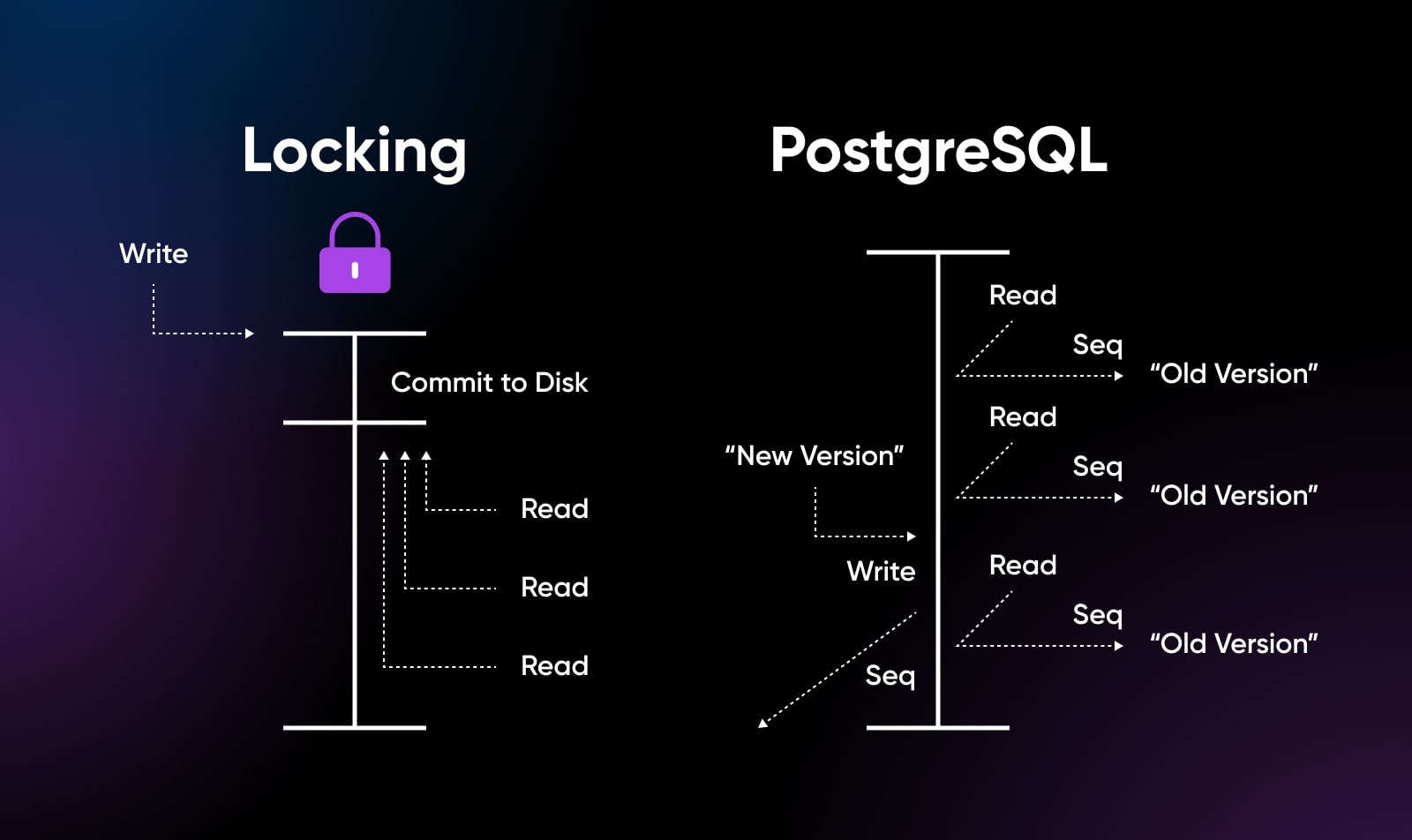
An space the place PostgreSQL notably excels is horizontal write scaling, permitting many concurrent periods to switch knowledge throughout distributed servers utilizing the MVCC mannequin.
This MVCC mannequin means glorious concurrency even for blended read-write workloads, permitting PostgreSQL databases to scale very massive throughput by way of replication. Writes proceed in parallel, then sync after.
MySQL InnoDB achieves related concurrency utilizing row-level locking reasonably than MVCC. however PostgreSQL’s structure has confirmed extra scalable beneath excessive write masses in testing.
Primarily, PostgreSQL finally helps better write scaling, albeit with extra server overhead. MySQL is lighter-weight for learn scaling.
PostgreSQL Vs. MySQL: Reliability And Knowledge Safety
PostgreSQL and MySQL present strong safety protections and reliability mechanisms – although PostgreSQL emphasizes sturdiness whereas MySQL focuses on excessive availability.
Entry Management And Encryption
PostgreSQL and MySQL additionally present consumer account controls, privileges administration, and community encryption capabilities for safety. Essential objects like SSL connections, password insurance policies, and role-based row-level safety apply equally.
Nonetheless, there are just a few variations round encryption:
- Native data-at-rest encryption: PostgreSQL 13 added pgcrypto module for file-system clear tablespace encryption. MySQL lacks native encryption however helps plugins.
- Light-weight row entry insurance policies: PostgreSQL has RLS and MASK for roles to handle row visibility all the way down to knowledge domains by way of insurance policies. MySQL can use views to get an analogous consequence, nevertheless it’s not as strong.
Whereas each RDBMS programs shield delicate knowledge by way of SSL/TLS encryption for consumer connections, PostgreSQL presents barely extra encryption cipher algorithms, exercise monitoring, and built-in entry management choices than MySQL.
PostgreSQL Reliability By way of WAL
PostgreSQL makes use of write-ahead logging (WAL), the place knowledge adjustments are recorded within the log earlier than the precise knowledge modifications happen.
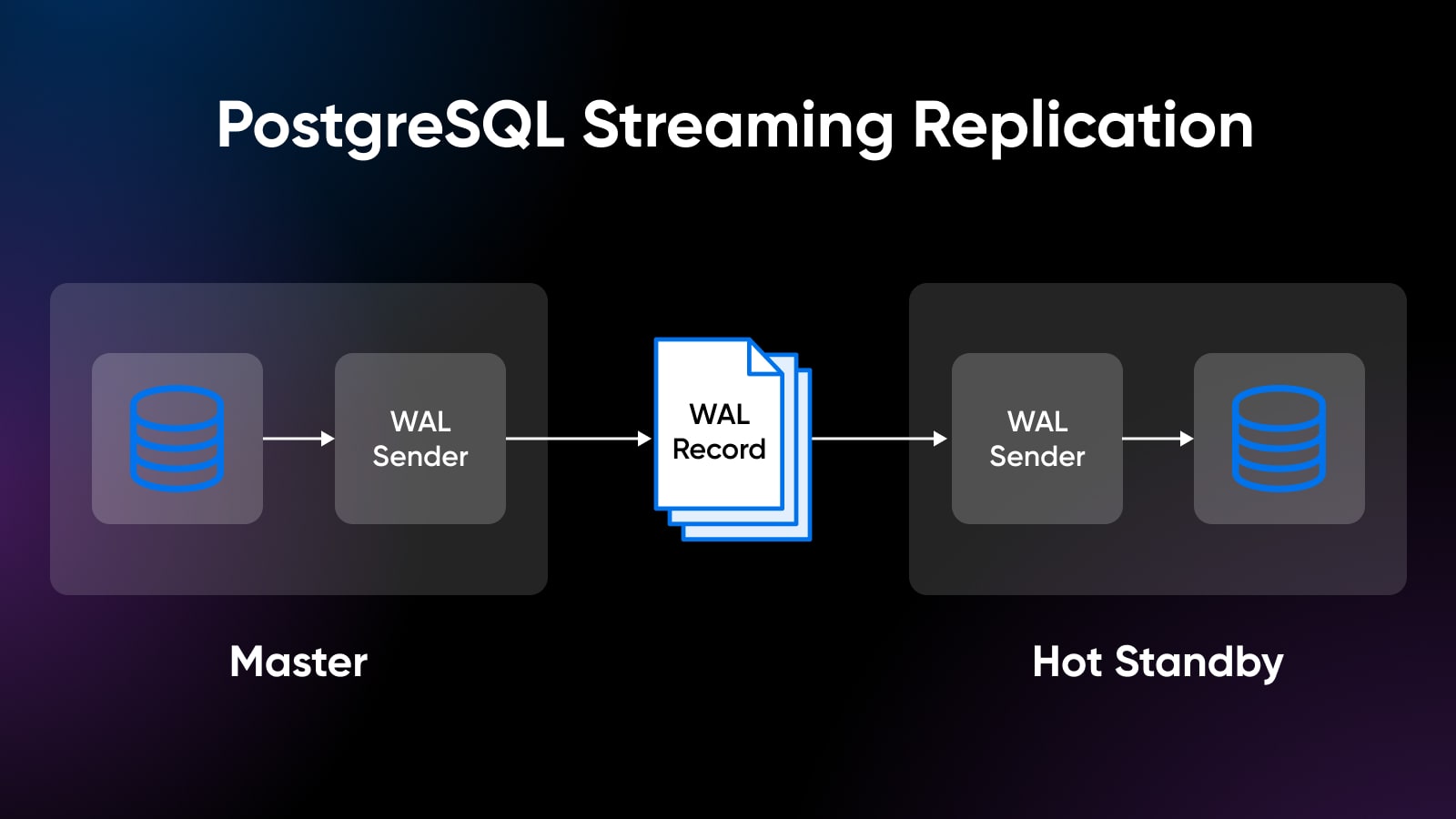
This protects towards knowledge loss, even in crashes or energy failures, stopping database corruption.
The WAL logs in PostgreSQL keep a constant chain of adjustments queued throughout transactions that may shortly replay and get well knowledge.
This mechanism powers options like streaming replication, parallel queries, and point-in-time restoration (PITR) to earlier states in time without having full backups.
General, WAL helps keep knowledge sturdiness ensures and efficiency boosts for crash restoration and replication.
MySQL Excessive Availability
For minimizing downtime, MySQL presents strong high-availability clustering that auto-fails over in case any single server crashes – with minimal interruption. The automated promotion of replicas and fast re-synchronization make outages a rare-case state of affairs.
Whereas MySQL 5.7 didn’t embody built-in excessive availability, MySQL 8 launched InnoDB cluster for automated failover between nodes.
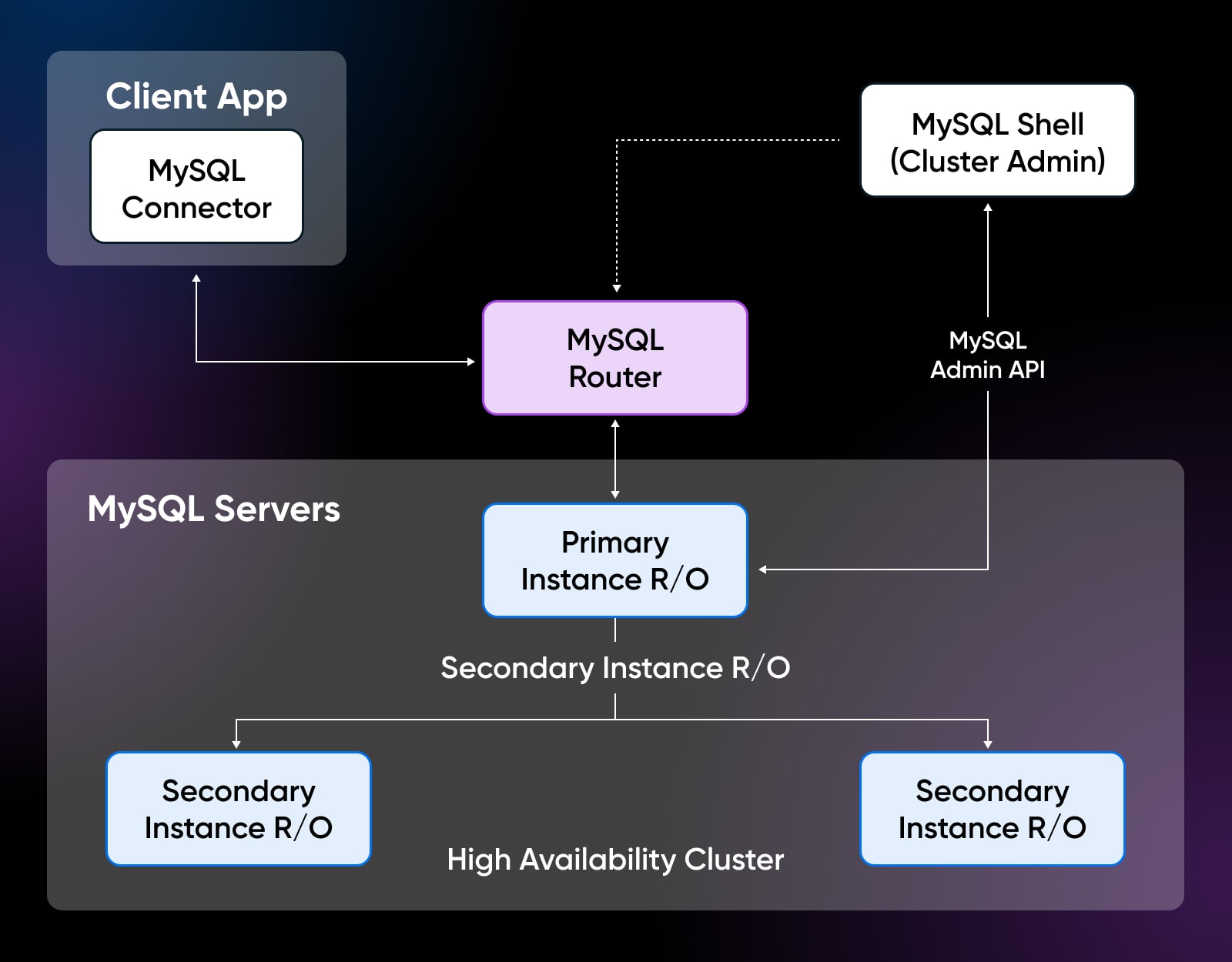
PostgreSQL additionally achieves excessive availability by way of replication instruments like Slony, Londiste, or pgpool-II, which offer trigger-based or middleware failover. Nonetheless, PostgreSQL lacks MySQL’s native clustering integration, regardless that you may obtain excessive availability.
So, in case your software mandates 100% server uptime with no handbook intervention, MySQL’s native clustering capabilities could serve higher. That’s additionally one of many the reason why WordPress, a content material administration system that powers 43% of the web, continues to make use of MySQL.
Given each databases’ lengthy histories and huge consumer bases, PostgreSQL and MySQL provide useful boards, documentation libraries, and third-party instruments. Nonetheless, some variations stand out.
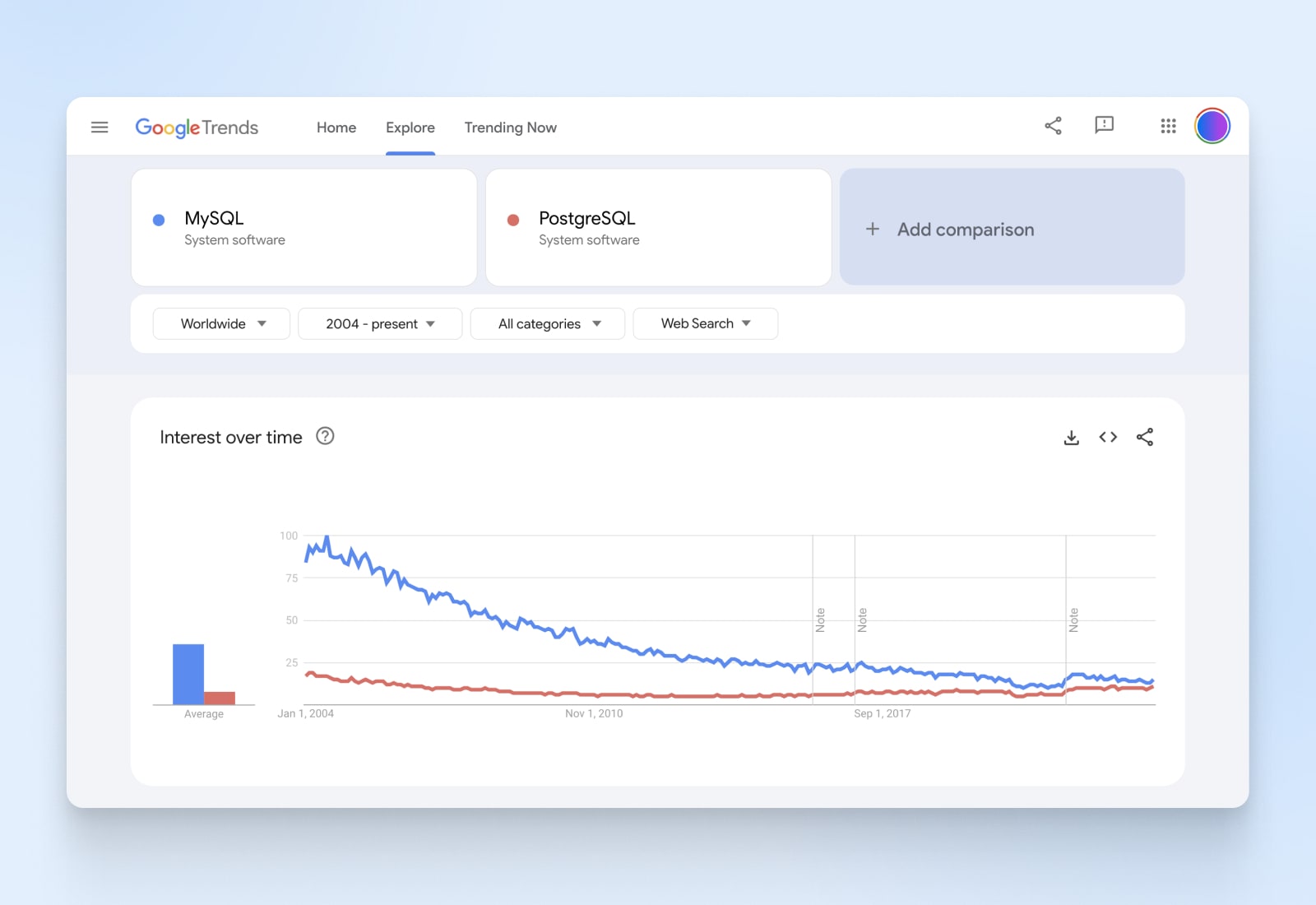
In response to Google Traits, the curiosity in MySQL has dropped considerably, inching nearer to PostgreSQL. Nonetheless, each databases nonetheless have a robust following and consumer base, giving them good group backing.
PostgreSQL Group
PostgreSQL growth is managed by the PostgreSQL International Growth Group – a group of open group builders collaborating worldwide. Hundreds of customers and contributors take part within the e mail lists, IRC channels, blogs, and occasions.
Additionally they host conferences like PGConf, bringing the Postgres group collectively periodically. General, a strong, succesful help ecosystem retains PostgreSQL progressing.
MySQL Group
As a massively fashionable open-source database, MySQL additionally enjoys on-line group help. The MySQL Developer Zone gives wealthy documentation and boards for troubleshooting points and subsequent steps. Massive conferences like Percona Stay talk about the most recent finest practices utilizing MySQL.
Oracle’s acquisition of MySQL additionally helped it get the much-needed funding into new releases and industrial help choices for these needing further help. Although not as grassroots as PostgreSQL, MySQL customers have nice group sources.
Evaluating Assist Depth
Each databases even have glorious group help networks. PostgreSQL gives extra superior technical recommendation and glorious documentation, given the database’s inherent complexity. Their documentation can be a bit cheeky, not like most different tech docs. Right here’s an excerpt:
“The primary century begins at 0001-01-01 00:00:00 AD, though they didn’t comprehend it on the time. This definition applies to all Gregorian calendar nations. There isn’t any century quantity 0, you go from -1 century to 1 century. Should you disagree with this, please write your criticism to: Pope, Cathedral Saint-Peter of Roma, Vatican.”
— PostgreSQL Documentation on EXTRACT, date_part
MySQL’s group presents a broader expertise perfecting newbie use circumstances like internet functions.
However for both database, count on engaged, caring consumer communities prepared to assist information utilization and development.
Typical Use Instances
Given the variations highlighted thus far, PostgreSQL and MySQL gravitate in direction of some distinct use circumstances. Nonetheless, each RDBMS programs typically work completely tremendous for internet functions studying and writing rows of information.
PostgreSQL Use Instances
PostgreSQL excels at very data-heavy analytic workloads equivalent to:
- Enterprise intelligence with advanced operating combination queries throughout hundreds of thousands of rows.
- Knowledge warehousing and reporting throughout many desk JOINS and situations.
- Knowledge science and machine studying require PostgreSQL’s array, hstore, JSON, and customized knowledge sorts.
- Geospatial and multidimensional evaluation by way of PostGIS and specialised processing. Examples embody real-time location knowledge, satellite tv for pc imagery, local weather knowledge, and geometry manipulation.
These reap the benefits of PostgreSQL flexibility.
Particular vertical use circumstances abound in authorized, medical, analysis, insurance coverage, authorities, and monetary verticals transferring towards large knowledge analytics.
Actual-world examples embody Reddit, Apple, Instagram, Johns Hopkins Hospital system genetics analysis, New York Instances promoting analytics, Amtrak rail buyer monitoring, Hole worker scheduling system, Skype name element information, and so forth.
MySQL Use Instances
MySQL focuses on pure velocity, simplicity of growth, and simple scalability inherent in internet and cell functions. Specific strengths shine for:
- Excessive-performance on-line transaction processing (OLTP) for e-commerce websites and internet apps needing excessive throughput on reads and writes touching quite a few discrete tables per row. Consider mature websites at scales equivalent to Airbnb, Twitter, Fb, and Uber.
- Massively multiplayer on-line (MMO) video games with an enormous participant base to help concurrently in close to real-time.
- Cellular functions and the Web of Issues (IoT) require compact databases to bundle regionally or embed in edge units with occasional syncing again to knowledge facilities.
- Software program-as-a-service (SaaS) multi-tenant platforms shortly scale out databases on demand whereas maintaining knowledge separated.
These functions prioritize availability and browse/write velocity at internet scale over deep analytics capabilities or knowledge science tooling. Again in 2016, Uber additionally moved from PostgreSQL again to MySQL, making this transition the discuss of the tech group for some time.
There are a lot of massive corporations that use MySQL, together with WordPress, Wikipedia, Fb, Google AdWords, Zendesk, Mint, Uber, Sq., Pinterest, Github, Netflix film looking, YouTube video metadata, and so forth.
Migrating From MySQL To PostgreSQL Or Vice Versa
Given the recognition of each databases, many builders could migrate between MySQL and PostgreSQL. What ought to they count on throughout this database migration course of?
General, migrating totally useful relational databases between MySQL and PostgreSQL works fairly easily usually, because of the wonderful migration instruments obtainable. Way more SQL syntax and capabilities overlap versus differ. Knowledge sorts normally translate nicely, though doing trial conversions helps.
Let’s discover some key challenges to handle:
Dealing with Knowledge Kind Modifications
When migrating schemas from MySQL to PostgreSQL or vice versa, pay shut consideration to any knowledge kind mismatches:
- MySQL’s AUTO_INCREMENT columns turn out to be SERIAL in PostgreSQL.
- PostgreSQL arrays want further syntax adjustments since there isn’t a related datatype in MySQL.
- Verify date/time knowledge conversions.
Take a look at migrations towards copies of manufacturing knowledge to validate constancy. Knowledge kind mismatches simply break functions if not addressed.
Saved Process Migration
Should you rely closely on saved procedures for enterprise logic, migrating them between MySQL and PostgreSQL requires rewriting code.
Key variations of their procedural languages, like delimiter syntax, typically break code portability. Additionally, verify permissions stay intact for manufacturing procedures.
So validate your migration totally and don’t assume capabilities come throughout cleanly between platforms.
Shopper Compatibility
Functions counting on PostgreSQL and MySQL consumer libraries additionally want reconfiguration when shifting environments:
- Replace connection strings.
- Change consumer library utilization.
- Redirect API calls to a brand new platform.
Altering the underlying database necessitates software adjustments too. Combine up to date connectivity into your migration testing guidelines.
Schema Modifications From RDBMS Options
Consider PostgreSQL’s desk inheritance, row-level safety, and fine-tuned consumer permissions versus MySQL views and triggers to see if logic ought to shift to new, improved constructs obtainable in every database. Performance-affecting options are likely to migrate cleaner, staying nearer to SQL requirements.
Software Code Modifications
Replace connection strings and drivers used, in fact. Moreover, optimize the efficiency strengths of every database. MySQL could leverage extra app-side joins and presentation logic, which is now purely in SQL on PostgreSQL. However, PostgreSQL could now implement enterprise rule approaches that had been beforehand solely attainable by way of MySQL triggers and saved procedures.
Luckily, many knowledge entry frameworks like Hibernate summary some variations away from builders by limiting uncovered proprietary syntax. Consider if ORM or consumer adjustments make sense, too.
Correct planning, evaluations of change affect, and staging environments decrease migration stress for efficiently harnessing the very best every database presents.
Use Migration Instruments
Luckily, some instruments assist transfer schemas and knowledge between MySQL and PostgreSQL with better ease:
- pgLoader: Fashionable knowledge migration utility for transferring to PostgreSQL.
- AWS SCT: Database converter for homogenous migrations.
These mechanically clean over many OS/atmosphere compatibility points whereas guaranteeing an identical knowledge throughout programs.
So depart your self conversion/check time, however make the most of automated instruments to swap databases.
What’s The Proper Database For You?
Deciding between PostgreSQL and MySQL relies upon considerably in your particular software necessities and group expertise, however just a few key questions can information your choice:
What kinds of knowledge will you be storing? If it’s essential work with extra advanced and interconnected knowledge, PostgreSQL’s versatile knowledge sorts and object-relational mannequin make that a lot less complicated.
How mission-critical is question efficiency and scalability? MySQL handles throughput higher for high-traffic internet apps that demand sooner reads. However PostgreSQL has confirmed stronger for blended read-write workloads on the enterprise scale.
What administration expertise does your group have? PostgreSQL rewards superior database experience, given its expansive configurability. MySQL is easier for admins with out glorious SQL expertise to get operating productively.
Platforms like DreamHost make internet hosting database servers straightforward and simple with VPS, devoted servers, and cloud internet hosting. DreamHost handles safety, and automated backups to streamline operations so you may concentrate on utilizing knowledge for enterprise insights.
So, let the DreamHost DBA group deal with deployment and administration when you architect the perfect knowledge platform in your development. PostgreSQL and MySQL provide open-source economics with enterprise reliability when powered by confirmed cloud consultants. One of the best database in your app probably awaits – strive at present!
Get Content material Delivered Straight to Your Inbox
Subscribe to our weblog and obtain nice content material identical to this delivered straight to your inbox.
[ad_2]