
[ad_1]
This publish is the ultimate installment of our Cloud Computing Foundations collection. Construct your abilities additional by taking our Cloud Computing by taking our certification course.
One of the necessary elements of the event lifecycle is knowing methods to safe the internet hosting setting that runs our internet apps. Our servers permit incoming connections from exterior methods over particular ports each time we deploy an online app. Server ports determine incoming and outgoing community site visitors.
To know server vulnerabilities, we’d like to consider the place communications happen.
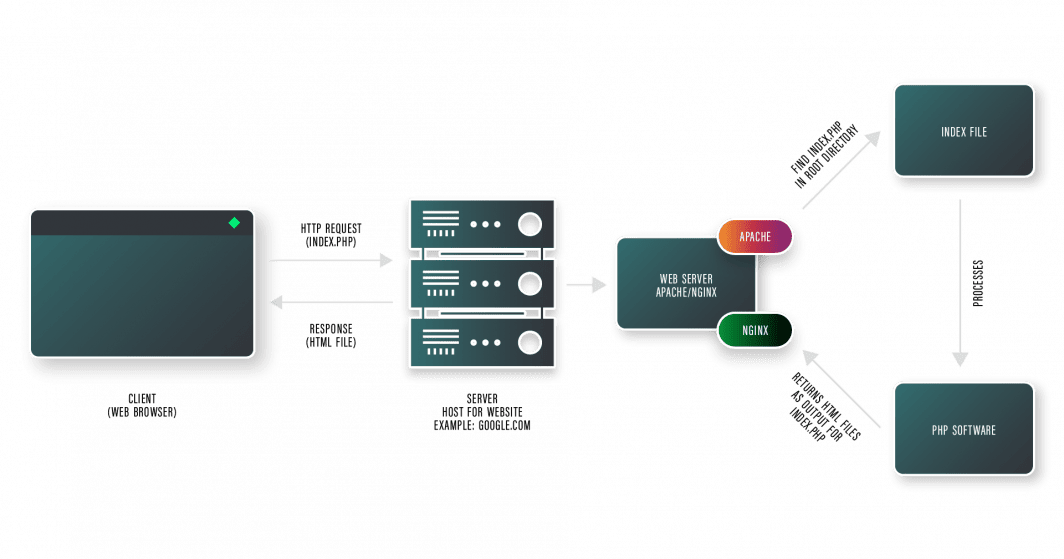
Within the instance above:
- A consumer (left), usually an online browser, sends an HTTP request to the server.
- The server receives the HTTP request and processes it.
- The area title is queried in opposition to a number of area title servers, normally managed by the area title registrar.
- The server retrieves or generates the requested content material and sends an HTTP response again to the consumer.
- The consumer receives the response and renders the content material.
Throughout this course of, in sure circumstances, connections to our servers might be from malicious computer systems seeking to exploit weaknesses in our server configurations. There are many the reason why a server is perhaps exploited.
Let’s check out some widespread server assaults.
Distributed Denial of Service Assaults (DDoS)
In a distributed denial of service (DDoS) assault an attacker makes an attempt to overload a focused server with a flood of HTTP requests. That is additionally known as an HTTP flood assault. Keep in mind, every time we make an HTTP request, our servers are tasked with responding to the request. If our servers don’t have the useful resource capability to satisfy the variety of incoming simultaneous requests, the online server will stall or crash. Transferring ahead, every subsequent HTTP request will fail, rendering the online server unreachable.
DDoS assaults are typically carried out by way of botnets. Botnets are a community of gadgets contaminated with malicious software program, also called malware, which is designed particularly to supply a flood of HTTP requests to a goal machine.
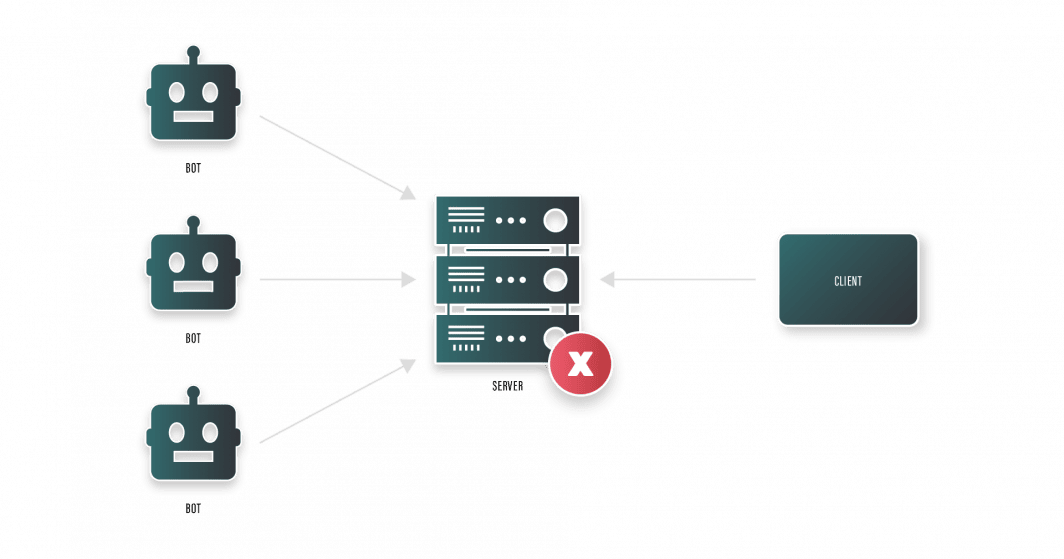
The above illustration gives an summary of how HTTP flood assaults work. On the precise aspect, we’ve got the consumer making a request to the server, however as a result of there are a number of bots additionally making requests to the server, thus draining the server’s sources, the consumer can’t hook up with the server.
Listing Traversal
A listing traversal is one other widespread exploit that typically targets poorly configured servers. All Net information are served straight from the Net Root Listing. Customers connecting to our servers through HTTP internet requests ought to solely be capable to entry particular information from the online root listing with out having the ability to navigate to or execute information from folders which might be greater within the listing construction. If this had been to occur, it might imply an attacker might achieve entry to essential system and configuration information and wreak havoc on the server.
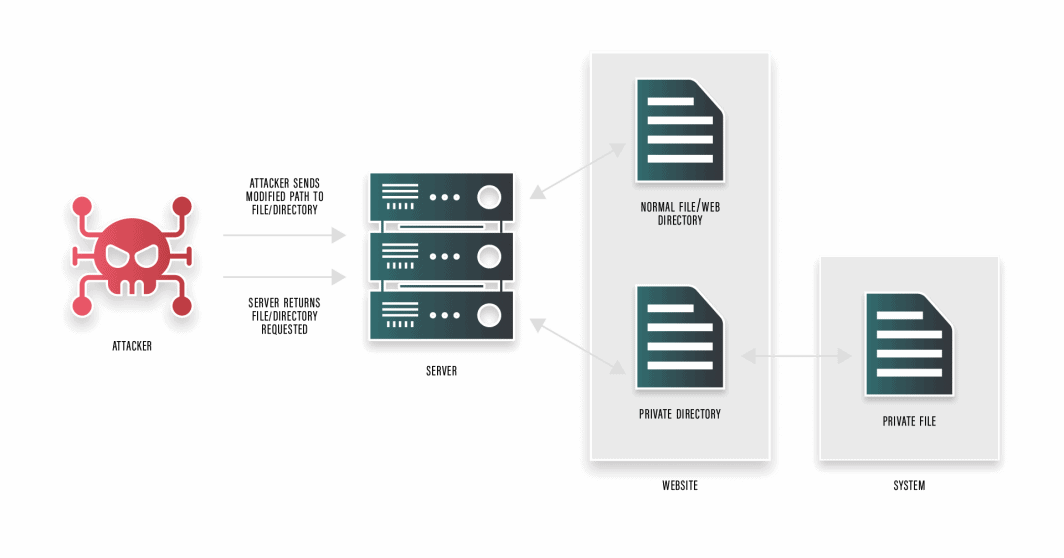
The above picture demonstrates how this assault works. The attacker submits a malicious HTTP request utilizing a modified URL, which incorporates the listing path to a system or configuration file. The server processes the request, and because of poor server configuration or utility design, can retrieve the system file and show its contents or supply code.
Brute Power Assault
A brute drive assault, additionally known as a dictionary assault or account takeover, is one other quite common assault whereby a malicious agent makes an attempt to achieve entry to a restricted entry level in your server. This restricted entry level is usually the server’s root account or one other account with root privileges. Attackers use malware to routinely submit quite a few login makes an attempt with routinely generated password and username mixtures primarily based on dictionary phrases.

The illustration above demonstrates how this assault works. On the left, the attacker submits repeated login makes an attempt generated from a thesaurus utilizing malware. If the right mixtures are discovered, the attacker will achieve entry to the server. Brute drive assaults might be extremely efficient—even when a server makes use of solely SSH key authentication.
Holding Your Server Safe
Listed here are some finest practices to contemplate when configuring and securing your servers:
- Maintain your working system and software program up-to-date with the most recent safety patches and updates.
- Disable or block any pointless companies or ports to reduce the assault floor.
- Restrict entry to your server by solely permitting licensed customers to attach and work together with it.
- Safe community site visitors through the use of encryption protocols similar to SSL or TLS.
- Have a sturdy backup and catastrophe restoration plan to reduce information loss and downtime.
- Implement sturdy passwords and multi-factor authentication to guard in opposition to unauthorized entry.
- Use firewalls to regulate incoming and outgoing community site visitors.
- Monitor server logs and community site visitors for suspicious exercise.
- Use intrusion detection and prevention methods to determine and stop assaults.
- Implement safety measures similar to file system permissions and entry controls to guard in opposition to unauthorized entry to delicate information.
Construct the abilities to reach cloud computing by taking our Introduction to Cloud Computing certification course.
[ad_2]