
[ad_1]
This system’s “Lacking Belief Fund” supplies a powerful case for an infusion of common revenues.
In response to the newest Social Safety Trustees Report, this system’s 75-year deficit elevated to three.61 p.c of taxable payroll in comparison with 3.42 p.c in 2022. The yr for depletion of Outdated-Age and Survivors Insurance coverage (OASI) belief fund belongings moved up one yr – from 2034 to 2033. Sure, the Incapacity Insurance coverage (DI) belief fund has adequate belongings to pay advantages for the complete 75-year interval and the date of exhaustion for the mixed OASDI belief funds is 2034. However combining the 2 methods would require a change within the regulation; therefore, beneath present regulation, the related date is 2033 – a decade from now (see Determine 1).
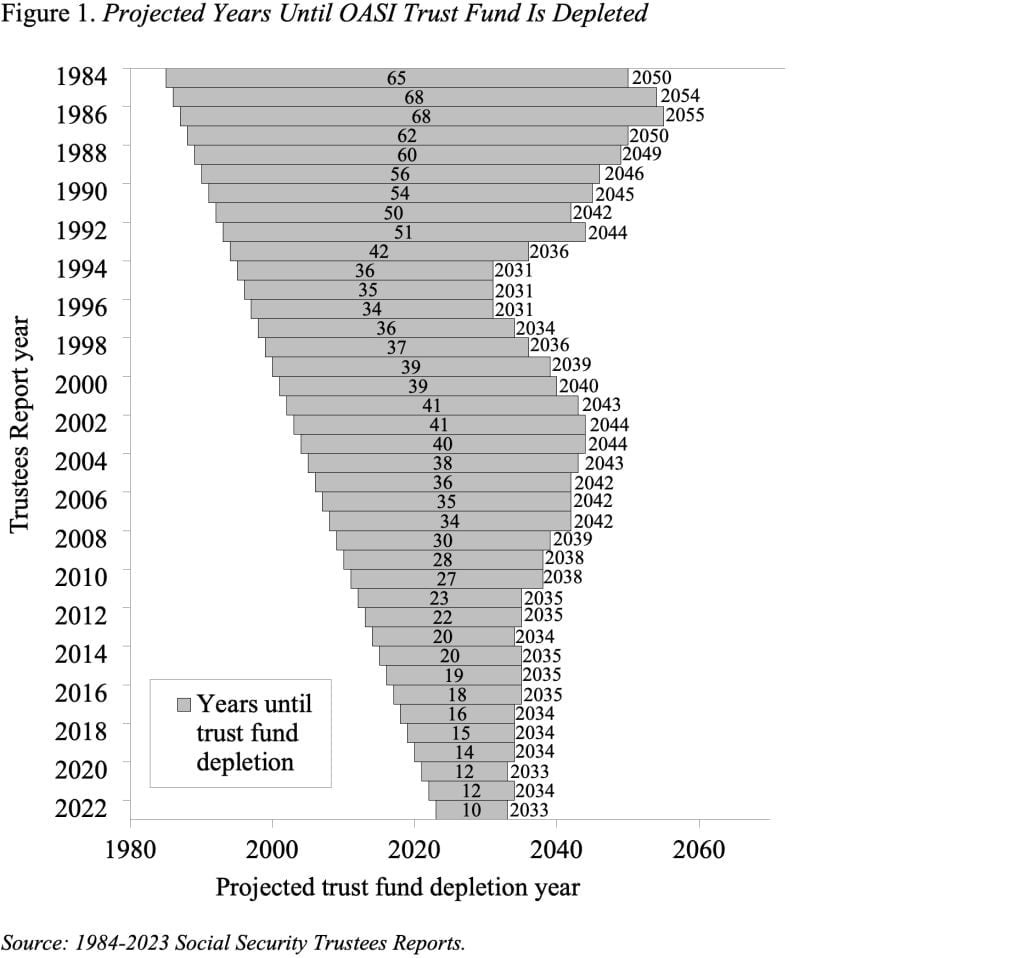
The truth that in 2033 Social Safety would be capable to pay solely 77 p.c of scheduled advantages ought to focus our collective minds. Considering of how to revive stability to this system shouldn’t be arduous; the Social Safety Actuaries publish an annual booklet with greater than 100 attainable advantages cuts or income will increase. Certainly, so much might be stated for sustaining a self-financed program the place retirees obtain advantages based mostly on their contributions, and annual outlays will not be topic to a congressional appropriations course of. And if the price of at present scheduled advantages merely exceeds what at this time’s employees are paying into the system, the normal proposals to scale back advantages or increase payroll taxes can be most related.
Nevertheless, the reason for the shortfall lies elsewhere. Particularly, this system’s “pay-as-you-go” strategy – excluding the current build-up and spend-down of the present modest belief fund – makes this system look costly. This financing strategy is the results of a coverage determination within the late Thirties to pay advantages far in extra of contributions for the early cohorts of employees. The choice basically gave away the belief fund that may have gathered and, importantly, gave away the curiosity on these contributions. The best option to see the implications of Social Safety’s “Lacking Belief Fund” is to think about the contribution charge required to finance this system’s retirement advantages beneath a funded retirement plan in comparison with a pay-as-you-go system (see Determine 2). Beneath a funded system, the mixed employer-employee contribution charge for a typical employee can be 11.2 p.c of earnings. Beneath our pay-as-you-go system, the full price is 14.9 p.c. The ensuing distinction of three.7 share factors (14.9 p.c minus 11.2 p.c) is as a result of presence of a belief fund that may pay curiosity in a completely funded system however is lacking within the pay-as-you-go system.
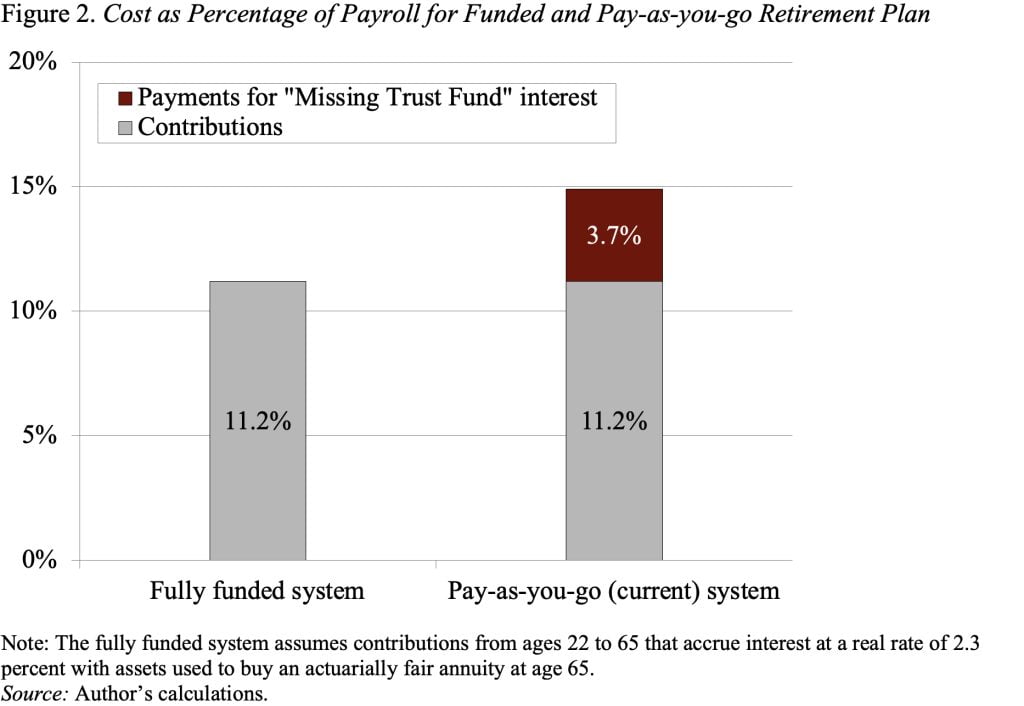
The approaching depletion of belief fund belongings is the best time to rethink this system’s financing construction and to think about whether or not a common income part could be applicable. The rationale for common income funding is that Social Safety prices are excessive, not as a result of this system is especially beneficiant, however as a result of the belief fund is lacking. If policymakers select to take care of Social Safety advantages at current-law ranges, little rationale exists for putting the whole burden of the Lacking Belief Fund on at this time’s employees by way of increased payroll taxes; that part might be financed extra equitably by way of the revenue tax.
[ad_2]