
[ad_1]
In Odessa, Texas, staff at a startup known as SolarCycle unload vehicles carrying end-of-life photovoltaic panels freshly picked from business photo voltaic farms throughout the US. They separate the panels from the aluminum frames and electrical containers, then feed them into machines that detach their glass from the laminated supplies which have helped generate electrical energy from daylight for a few quarter of a century.
Subsequent, the panels are floor, shredded and subjected to a patented course of that extracts the precious supplies — principally silver, copper and crystalline silicon. These parts will likely be bought, as will the lower-value aluminum and glass, which can even find yourself within the subsequent era of photo voltaic panels.
This course of gives a glimpse of what may occur to an anticipated surge of retired photo voltaic panels that can stream from an trade that represents the fastest-growing supply of power within the U.S. In the present day, roughly 90 % of panels within the U.S. which have misplaced their effectivity on account of age, or which are faulty, find yourself in landfills as a result of that possibility prices a fraction of recycling them.
However recycling advocates within the U.S. say elevated reuse of helpful supplies, comparable to silver and copper, would assist increase the round economic system, during which waste and air pollution are lowered by always reusing supplies. In line with a 2021 report by the Nationwide Renewable Vitality Laboratory (NREL), recycling PV panels may additionally reduce the chance of landfills leaking toxins into the atmosphere; improve the soundness of a provide chain that’s largely depending on imports from Southeast Asia; decrease the price of uncooked supplies to photo voltaic and different sorts of producers; and increase market alternatives for U.S. recyclers.
U.S. photo voltaic panels on account of retire by 2030 would cowl about 3,000 American soccer fields.
In fact, reusing degraded however still-functional panels is a fair higher possibility. Thousands and thousands of those panels find yourself in growing nations, whereas others are reused nearer to residence. For instance, SolarCycle is constructing an influence plant for its Texas manufacturing unit that can use refurbished modules.
The prospect of a future glut of expired panels is prompting efforts by a handful of photo voltaic recyclers to deal with a mismatch between the present buildup of renewable power capability by utilities, cities, and personal firms — hundreds of thousands of panels are put in globally yearly — and a scarcity of amenities that may deal with this materials safely when it reaches the top of its helpful life, in about 25 to 30 years.
Photo voltaic capability throughout all segments within the U.S. is predicted to rise by a mean of 21 % a yr from 2023 to 2027, in accordance with the most recent quarterly report from the Photo voltaic Vitality Industries Affiliation and the consulting agency Wooden Mackenzie. The anticipated improve will likely be helped by the landmark Inflation Discount Act of 2022 which, amongst different helps for renewable power, will present a 30 % tax credit score for residential photo voltaic installations.
The world lined by photo voltaic panels put in within the U.S. as of 2021 and on account of retire by 2030 would cowl about 3,000 American soccer fields, in accordance with an NREL estimate. “It’s an excellent little bit of waste,” mentioned Taylor Curtis, a authorized and regulatory analyst on the lab. However the trade’s recycling fee, at lower than 10 %, lags far behind the upbeat forecasts for the trade’s development.
By 2050, the worth of uncooked supplies recoverable from photo voltaic panels may exceed $15 billion.
Jesse Simons, a co-founder of SolarCycle, which employs about 30 folks and commenced operations in December, mentioned stable waste landfills usually cost $1 to $2 to simply accept a photo voltaic panel, rising to round $5 if the fabric is deemed hazardous waste. Against this, his firm costs $18 per panel. Purchasers are keen to pay that fee as a result of they could be unable to discover a landfill licensed to simply accept hazardous waste and assume authorized legal responsibility for it, and since they need to reduce the environmental impression of their previous panels, mentioned Simons, a former Sierra Membership govt.
SolarCycle offers its purchasers with an environmental evaluation that exhibits the advantages of panel recycling. For instance, recycling aluminum makes use of 95 % much less power than making virgin aluminum, which bears the prices of mining the uncooked materials, bauxite, then transporting and refining it.
The corporate estimates that recycling every panel avoids the emissions of 97 kilos of CO2; the determine rises to greater than 1.5 tons of CO2 if a panel is reused. Beneath a proposed Securities and Alternate Fee rule, publicly held firms will likely be required to reveal climate-related dangers which are more likely to have a fabric impression on their enterprise, together with their greenhouse fuel emissions.
Stripped from photo voltaic panels on the SolarCycle plant, aluminum is bought at a close-by metallic yard. Glass is bought for just some cents per panel for reuse in fundamental merchandise comparable to bottles, however Simons hopes he’ll ultimately have sufficient of it to promote for the next worth to a producer of recent photo voltaic panel sheets.
As of July, California had just one recycling plant that accepted photo voltaic panels.
Crystalline silicon, used as a base materials in photo voltaic cells, can be value recovering, he mentioned. Though it have to be refined to be used in future panels, its use avoids the environmental impacts of mining and processing new silicon.
SolarCycle is one among solely 5 firms within the U.S. listed by the SEIA as able to offering recycling providers. The trade stays in its infancy and continues to be determining methods to generate income from recovering after which promoting panel parts, in accordance with the U.S. Environmental Safety Company. “Components of this recycling course of may be present in the US, however it isn’t but occurring on a big scale,” the EPA mentioned in an overview of the trade.
In 2016, the Worldwide Renewable Vitality Company (IRENA) forecast that by the early 2030s, the worldwide amount of decommissioned PV panels will equal some 4 % of the variety of put in panels. By the 2050s, the quantity of photo voltaic panel waste will rise to at the least 5 million metric tons a yr, the company mentioned. China, the world’s largest producer of photo voltaic power, is predicted to have retired a cumulative whole of at the least 13.5 million metric tons of panels by 2050, by far the most important amount amongst main solar-producing nations and almost twice the quantity the U.S. will retire by that point, in accordance with the IRENA report.
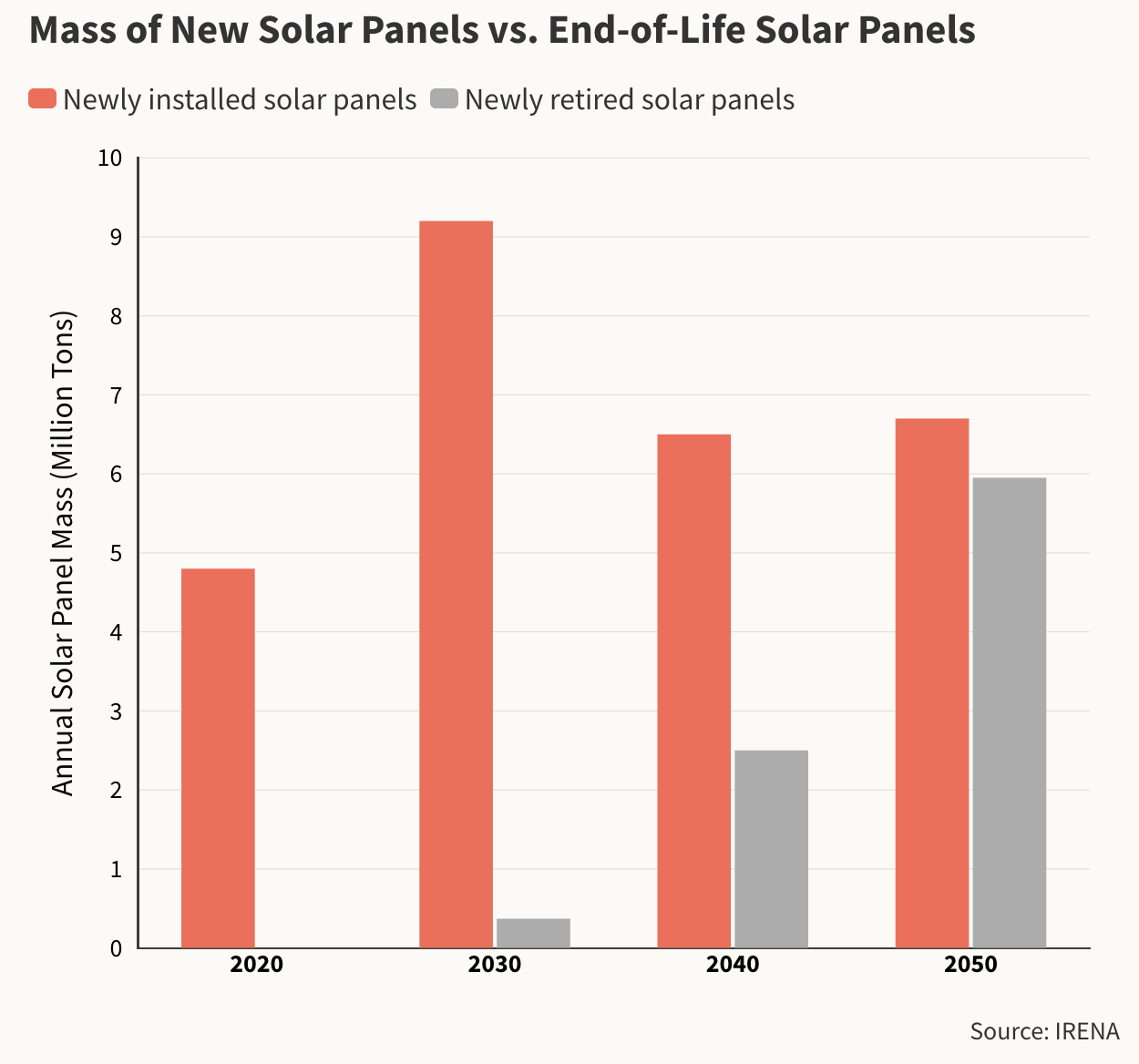
The uncooked supplies technically recoverable from PV panels globally may cumulatively be value $450 million (in 2016 phrases) by 2030, the report discovered, about equal to the price of uncooked supplies wanted to provide some 60 million new panels, or 18 gigawatts of power-generation capability. By 2050, the report mentioned, recoverable worth may cumulatively exceed $15 billion.
For now, although, photo voltaic recyclers face vital financial, technological and regulatory challenges. A part of the issue, says NREL’s Curtis, is an absence of information on panel recycling charges, which hinders potential coverage responses which may present extra incentives for solar-farm operators to recycle end-of-life panels reasonably than dump them.
One other downside is that the Toxicity Attribute Leaching Process — an EPA-approved technique used to find out whether or not a product or materials comprises hazardous parts that would leach into the atmosphere — is thought to be defective. Consequently, some photo voltaic farm homeowners find yourself “over-managing” their panels as hazardous with out making a proper hazardous-waste willpower, Curtis mentioned. They find yourself paying extra to eliminate them in landfills permitted to deal with hazardous waste or to recycle them.
The Worldwide Vitality Company assessed whether or not photo voltaic panels that include lead, cadmium and selenium would have an effect on human well being if dumped in both hazardous-waste or municipal landfills and decided the chance was low. Nonetheless, the company mentioned in a 2020 report, its findings didn’t represent an endorsement of landfilling: Recycling, it said, would “additional mitigate” environmental issues.
NREL is learning another course of for figuring out whether or not panels are hazardous. “We have to determine that out as a result of it’s positively impacting the legal responsibility and the price to make recycling extra aggressive,” Curtis mentioned.
Regardless of these uncertainties, 4 states not too long ago enacted legal guidelines addressing PV module recycling. California, which has essentially the most photo voltaic installations, permits panels to be dumped in landfills, however solely after they’ve been verified as non-hazardous by a delegated laboratory, which might price upwards of $1,500. As of July, California had just one recycling plant that accepted photo voltaic panels.
In Washington state, a regulation designed to supply an environmentally sound technique to recycle PV panels is because of be carried out in July 2025; New Jersey officers anticipate to challenge a report on managing PV waste this spring; and North Carolina has directed state environmental officers to check the decommissioning of utility scale photo voltaic tasks. (North Carolina requires photo voltaic panels to be disposed of as hazardous waste in the event that they include heavy metals comparable to silver or — within the case of older panels — hexavalent chromium, lead, cadmium and arsenic.)

Within the European Union, end-of-life photovoltaic panels have, since 2012, been handled as digital waste beneath the EU’s waste electrical and digital gear directive, generally known as WEEE. The directive requires all member states to adjust to minimal requirements, however the precise fee of e-waste recycling varies from nation to nation, mentioned Marius Mordal Bakke, senior analyst for photo voltaic provider analysis at Rystad Vitality, a analysis agency headquartered in Oslo, Norway. Regardless of this regulation, the EU’s PV recycling fee isn’t any higher than the U.S. fee — round 10 % — largely due to the problem of extracting helpful supplies from panels, Bakke mentioned.
However he predicted that recycling will change into extra prevalent when the variety of end-of-life panels rises to the purpose the place it presents a enterprise alternative, offering recyclers with helpful supplies they’ll promote. Governments will help pace that transition, he added, by banning the disposal of PV panels in landfills and offering incentives comparable to tax breaks to anybody who makes use of photo voltaic panels.
“In some unspecified time in the future sooner or later, you’re going to see sufficient panels being decommissioned that you just sort of have to start out recycling,” Bakke mentioned. “It would change into worthwhile by itself no matter commodity costs.”
[ad_2]